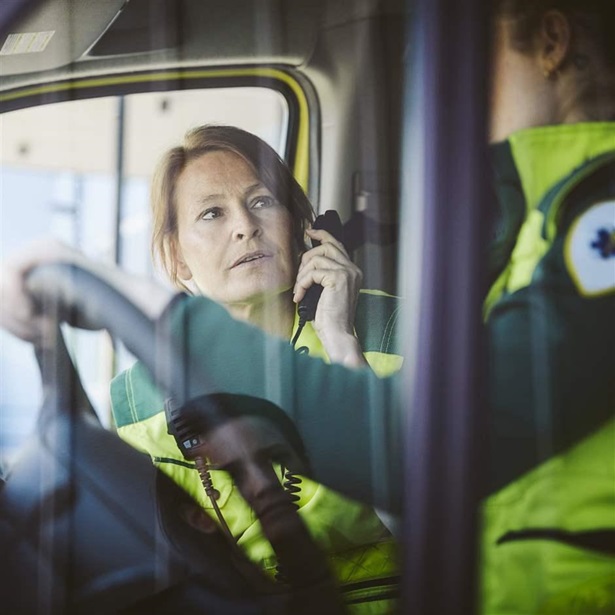
State Leaders Agree Behavioral Health a Top Bipartisan Concern in 2024
28 governors prioritize improving mental health and substance use disorder care systems in year-opening addresses.

President Joe Biden reflected in his State of the Union in March on the COVID-19 pandemic and how it had wreaked havoc on people’s day-to-day lives, spurring “a mental health crisis of isolation and loneliness.” Data supports this: As the pandemic unfolded, one 2021 study found that about 4 in 10 adults reported symptoms of anxiety or depression, four times pre-pandemic levels.
People had struggled to access adequate behavioral health support long before 2020, as these systems have been historically under-resourced and fragmented. As one sign of the worsening of these problems, the suicide rate had increased 30% between 2000 and 2020 and has continued to rise in recent years. In fact, the pandemic exposed and exacerbated existing faults with an influx of people needing care. Overburdened emergency departments, for instance, are too often a landing place for people with mental health emergencies. But they tend to be ill-equipped to serve people in distress, with waiting times for psychiatric hospitalization often lasting weeks, or even months.
Fortunately, recent months have seen growing bipartisan momentum among state leaders to invest in behavioral health care. A review by The Pew Charitable Trusts shows that 28 governors identified behavioral health as a priority in their State of the State addresses in early 2024.
Several specifically committed to strengthening the 988 Suicide and Crisis Lifeline, which provides emergency mental health counseling and connections to care, as well as implementing more crisis response teams and providing more alternative treatment options.
“We started this journey with 36 mobile crisis units, with a goal of doubling them,” said Virginia Governor Glenn Youngkin (R). “And I can tell you, today we are at 97 mobile crisis units in the commonwealth, and still going strong.”
The entire chain—from who is called in the event of an emergency to who responds in such a situation, and where a person in need of immediate intervention and often follow-up services and supports can go—is referred to as the “crisis continuum of care.”
Although continuity is essential for people in need of behavioral health care, it can be difficult to provide or receive because of the current patchwork of response systems throughout communities. For example, Iowa Governor Kim Reynolds (R) acknowledged in her Jan. 9 address “little to no coordination” across the state’s 13 mental health and 19 substance use regions.
“Our state is filled with capable professionals who care about getting Iowans the support they need,” she said. “But their talent and dedication are short-changed by a fractured system that makes coordination almost impossible.”
Reynolds is one of several governors who are working to unify their state’s behavioral health care efforts. Maine is another state focused on making progress this year. “I propose that we establish a network of crisis receiving centers across Maine so that any person suffering a mental health crisis can get prompt and appropriate care, instead of being alone or languishing in an emergency department or a jail, as is too often the case,” said Governor Janet Mills (D).
People should be able to access proven, effective care regardless of who they are, where they live, or how they request it. Through investment, policy changes, and coordination of local response efforts, more state leaders can play a critical role in ensuring their residents receive quality behavioral health care. These state leaders, from Washington to Maine, are paving the way.
Julie Wertheimer directs research and policy for The Pew Charitable Trusts’ mental health and justice partnerships project.
MORE FROM PEW
Explore Pew’s new and improved
Fiscal 50 interactive
Your state's stats are more accessible than ever with our new and improved Fiscal 50 interactive:
- Maps, trends, and customizable charts
- 50-state rankings
- Analysis of what it all means
- Shareable graphics and downloadable data
- Proven fiscal policy strategies
Welcome to the new Fiscal 50
Key changes include:
- State pages that help you keep track of trends in your home state and provide national and regional context.
- Interactive indicator pages with highly customizable and shareable data visualizations.
- A Budget Threads feature that offers Pew’s read on the latest state fiscal news.