Kentucky's 2014 Juvenile Justice Reform
New law will strengthen community supervision and reduce secure confinement
Overview
After successful adult corrections reforms in 2011, Kentucky adopted comprehensive legislation in 2014 that was based on recommendations from a bipartisan, interbranch task force. Reforms enacted through Senate Bill 200 are expected to save Kentucky taxpayers as much as $24 million over five years while protecting public safety, holding juvenile offenders accountable for their actions, and improving outcomes for these youth and their families.
Highlights
Problem
Kentucky spends a significant amount of money to send low-level status and public offenders to out-of-home residential placements. More than half of the $102 million budget of the Department of Juvenile Justice (DJJ) is spent on secure and nonsecure residential facilities, where the majority of beds cost $87,000 per year. In addition, the Department for Community Based Services spent an estimated $6 million in fiscal year 2012 for out-of-home placement of status offenders.
Findings
The Task Force found that the majority of youth in out-of-home placements were lower-level offenders. They also found that the length of time spent out-of-home increased 31 percent for probation and court order violators and 21 percent for misdemeanor offenders between 2002 and 2012, and the length of time they spent in out-of-home facilities was similar regardless of the seriousness of their offenses.
Reforms
The task force developed recommendations to focus expensive out-of-home facilities on the most serious offenders. Incorporated into S.B. 200, the reforms restrict the commitment of lower-level offenders and how long they may be placed out-of-home; increase and strengthen evidence-based programs; create a fiscal incentive program; and establish an Oversight Council. S.B. 200 passed both houses of the Legislature and was signed into law by Governor Steve Beshear in April 2014.
Impact
The reforms are projected to reduce DJJ’s out-of-home population by more than one-third. The law also creates an enhanced pre-court process that will likely reduce the number of status and public offenders entering the court system. The reforms are expected to save Kentucky as much as $24 million over five years (Figure 1.) These savings may then be reinvested to expand community-based programs and proven practices to improve outcomes for children and families.
Figure 1
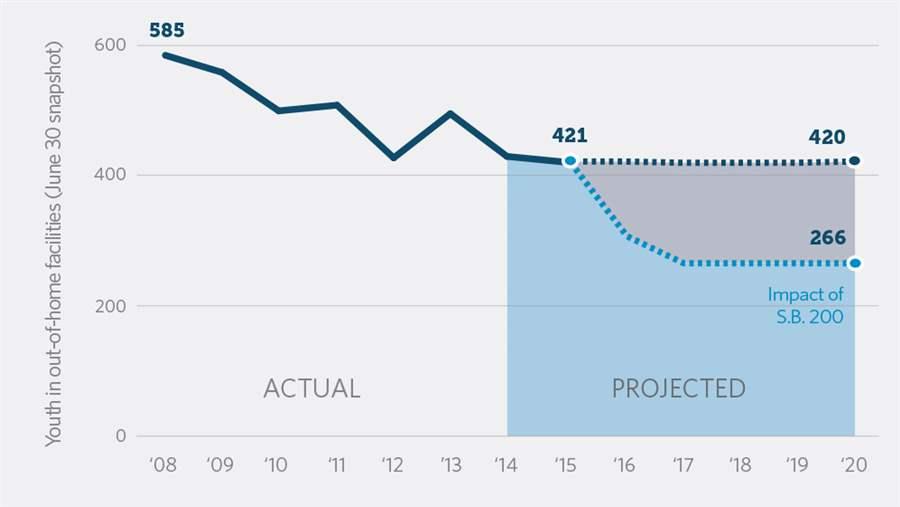 ©
© Reforms Expected to Reduce Out-of-home Population
Kentucky stands to save up to $24 million over 5 years.
Source: Kentucky Department of Juvenile Justice (historical data), Pew analysis (projected data).






