Health Impact Assessments
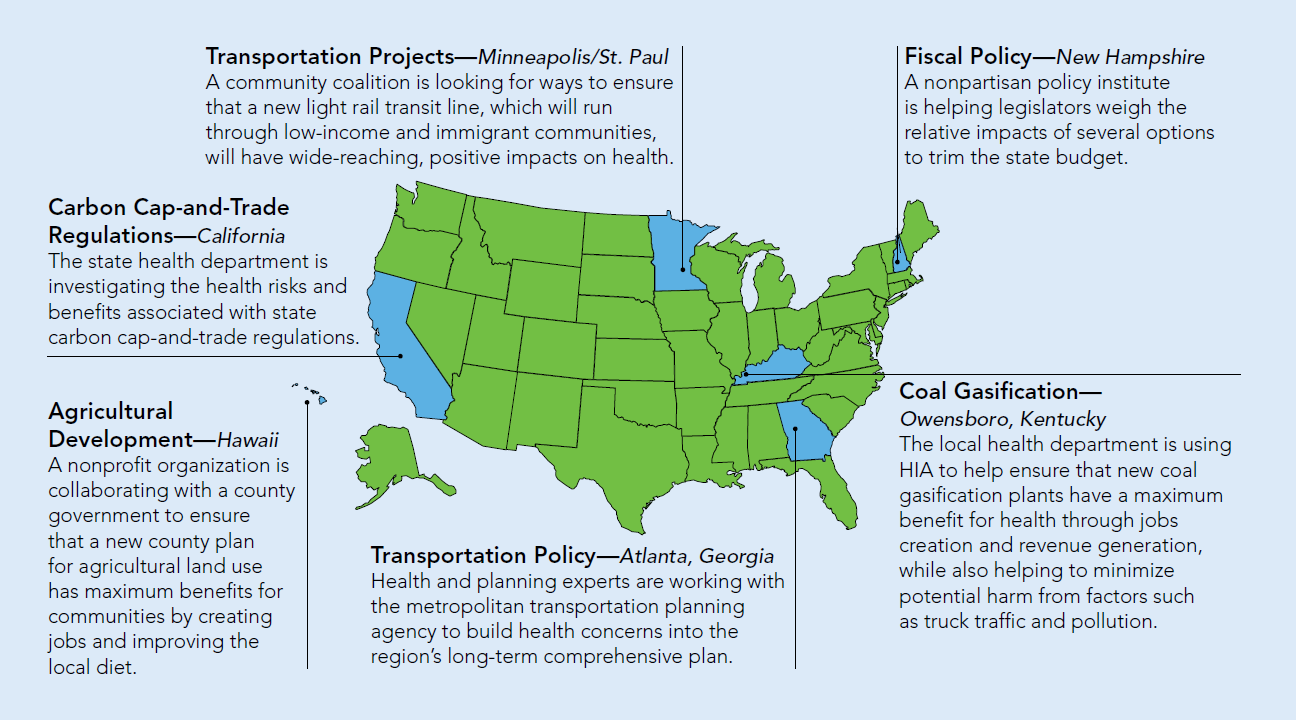
A Selection of HIAs Current Supported by the Health Impact Project
Preventable health problems, including many cases of heart disease, diabetes, asthma and injuries, are taking a huge toll on American families. For the first time in U.S. history, data suggest that today's children may live shorter lives than their parents. These problems also threaten our nation's economic vitality. Heart disease and diabetes alone now account for more than 700,000 deaths in the United States annually and cost the nation over $650 billion in medical expenses, disability, missed work and financial losses associated with premature death. These costs are rising every year.
To improve Americans' health, the root causes of these illnesses must be addressed. By factoring health consequences into the process when drafting new laws and regulations, building a major roadway, planning for a city's growth or developing a school curriculum, policy makers can capitalize on hidden opportunities to improve health, save on health-related costs and use limited resources more wisely. Health Impact Assessment (HIA) is a practical, evidence-driven tool to accomplish these goals. Many nations, large lending banks and major industries such as oil, gas and mining are adopting HIA to improve health, control costs and build trust with communities.
The Health Impact Project, a collaboration of the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation and The Pew Charitable Trusts, is a national initiative designed to promote the use of health impact assessments (HIAs) as a decision-making tool for policymakers. HIAs use a flexible, data-driven approach that identifies the health consequences of new policies and develops practical strategies to enhance their health benefits and minimize adverse effects.
Full Report: Health Impact Assessment: Bringing Public Health Data to Decision Making.






