How States Are Improving Tax Incentives for Jobs and Growth
A national assessment of evaluation practices
Overview
Tax incentives—including credits, exemptions, and deductions—are one of the primary tools that states use to try to create jobs, attract new businesses, and strengthen their economies. Incentives are also major budget commitments, collectively costing states billions of dollars a year. Given this importance, policymakers across the country increasingly are demanding high-quality information on the results of tax incentives.
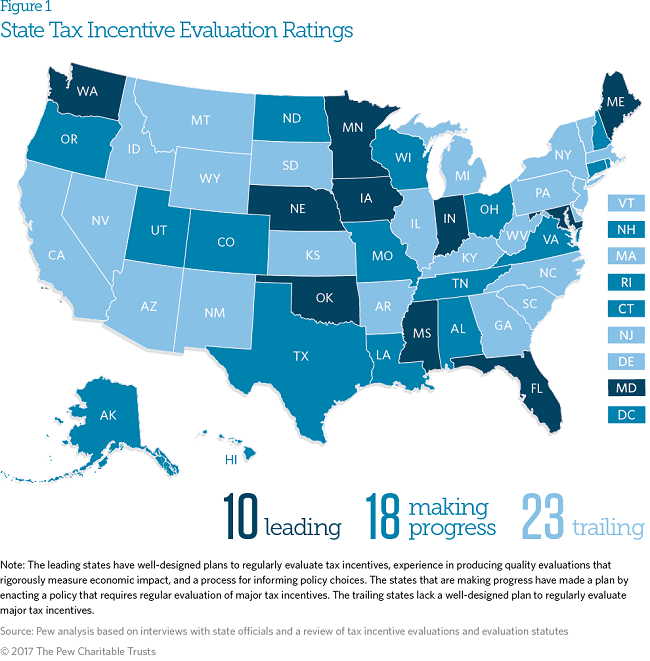
In the last five years, 27 states and the District of Columbia have made progress in gathering evidence on the results of their economic development tax incentives. Ten of these states are leaders in tax incentive evaluation. They have well-designed plans for regular reviews, experience in producing quality evaluations, and a process for informing policy choices. No state met these three criteria five years ago.
Download the full report. (PDF)
The 10 states that excel—Florida, Indiana, Iowa, Maine, Maryland, Minnesota, Mississippi, Nebraska, Oklahoma, and Washington—rigorously measure the economic and fiscal impact of their programs. As a result, policymakers have realistic, reliable information on the effectiveness of incentives.
And when lawmakers have this information, they use it. Policymakers in numerous states, including Florida, Indiana, Maryland, and Washington, have made changes to incentives that were consistent with the findings or recommendations of evaluations. Changes both large and small—from ending ineffective programs to subtly modifying the design or administration of incentives—can greatly improve the effectiveness of state economic development efforts.
Building on earlier research by The Pew Charitable Trusts, this report identifies best practices for effectively evaluating tax incentives. Specifically, Pew recommends that states take three steps:
- Make a plan. Lawmakers need to put processes in place to regularly evaluate the results of major tax incentives. Well-designed evaluation plans ensure that the state’s full portfolio of incentives is examined, that nonpartisan staff with relevant expertise are tasked with the analyses, and that the reviews take place on a strategic schedule.
- Measure the impact. High-quality evaluations carefully assess the results of incentives for the state’s budget and economy. To do so, evaluators must estimate the extent to which incentives successfully changed business behavior, as opposed to rewarding what companies would have done anyway.
- Inform policy choices. Lawmakers and executive branch officials should use the findings of evaluations to improve the effectiveness of tax incentives. Policy improvements are more likely when states have a formal process that ensures lawmakers will consider the results—for example, by holding legislative hearings on evaluations.
Pew staff assessed each state on the extent to which it has taken each of these steps. To do so, Pew staff gathered and analyzed tax incentive evaluations and other state documents. We also interviewed state officials and other experts from all 50 states and the District of Columbia. Based on this research, states were rated as “leading,” “making progress,” or “trailing.” The leading states have achieved success on all three criteria, while those that are making progress have put in place a plan for regular evaluation.
Taken as a whole, more states are evaluating incentives, with far more rigor and policy impact, than were doing so just a few years ago. In 2015 and 2016, 13 states approved laws requiring regular evaluations. But all states still have room to improve. This report describes the strengths and weaknesses of each state’s approach to evaluating incentives, and offers options for how states can enhance their efforts. The 23 states that are still trailing can start by making a well-designed evaluation plan. States that have taken that first step can offer lawmakers high-quality analysis that helps inform their policy choices.
Evaluating incentives well takes time, effort, and persistence. The payoff, though, is worth it: Policymakers have the information they need to ensure that economic development tax incentives achieve strong results for states’ budgets, businesses, and workers.