Mississippi's 2014 Corrections and Criminal Justice Reform
Legislation to improve public safety, ensure certainty in sentencing, and control corrections costs
In 2014, Mississippi enacted sentencing and corrections reforms that place it at the forefront of states employing research-driven criminal justice policies to produce a greater public safety return on corrections spending. The Corrections and Criminal Justice Task Force, a bipartisan, interbranch group of state and local officials, developed the reform package, H.B. 585, and The Pew Charitable Trusts provided intensive technical assistance.
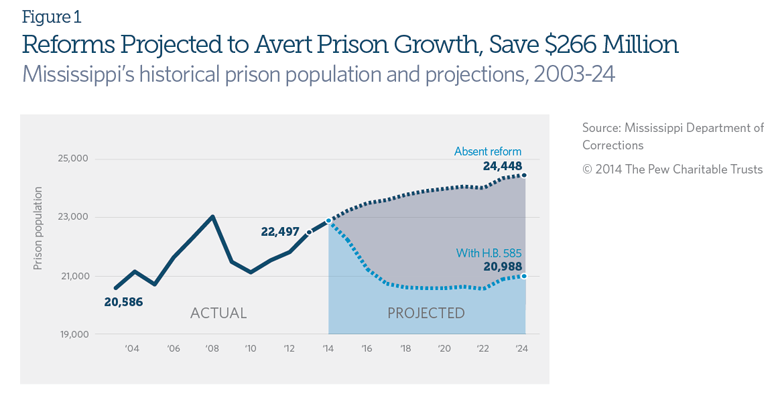
Problem: Between 1983 and 2013, Mississippi’s prison population grew by 300 percent to more than 22,400 inmates. Data show that in 2012—the latest year for which figures are available—Mississippi had the second-highest imprisonment rate in the country. Without a change in policy, the state projected that the incarcerated population would grow by 1,951 inmates at a cost of $266 million over 10 years.
Findings: An extensive review of data by the task force revealed that nonviolent offenders and those revoked for probation or parole violations accounted for a large and growing share of Mississippi’s prison population. In addition, a 28 percent increase in sentence lengths from 2002 to 2012, though partially offset by expanded early release options, lead to longer average prison stays. Finally, courts had few alternatives at their disposal for lower-level nonviolent offenders.
Reforms: The task force developed 19 policy recommendations aimed at refocusing prison space on violent and career criminals, strengthening community supervision, and ensuring certainty and clarity in sentencing. These recommendations were codified in H.B. 585, which passed with large bipartisan majorities in both legislative chambers and was signed into law by Governor Phil Bryant on March 31, 2014.
Impact: The criminal justice reform legislation is expected to avert all of Mississippi’s projected prison growth over the coming decade, saving taxpayers at least $266 million through 2024, while safely reducing the inmate population below current levels. The legislation also will restore certainty and clarity to Mississippi’s sentencing system and allow corrections dollars to be redirected into community supervision and programs proved to reduce recidivism.