WTO Members Not Off the Hook on Limiting Fishing Subsidies
Governments can still improve ocean health by strengthening the existing agreement
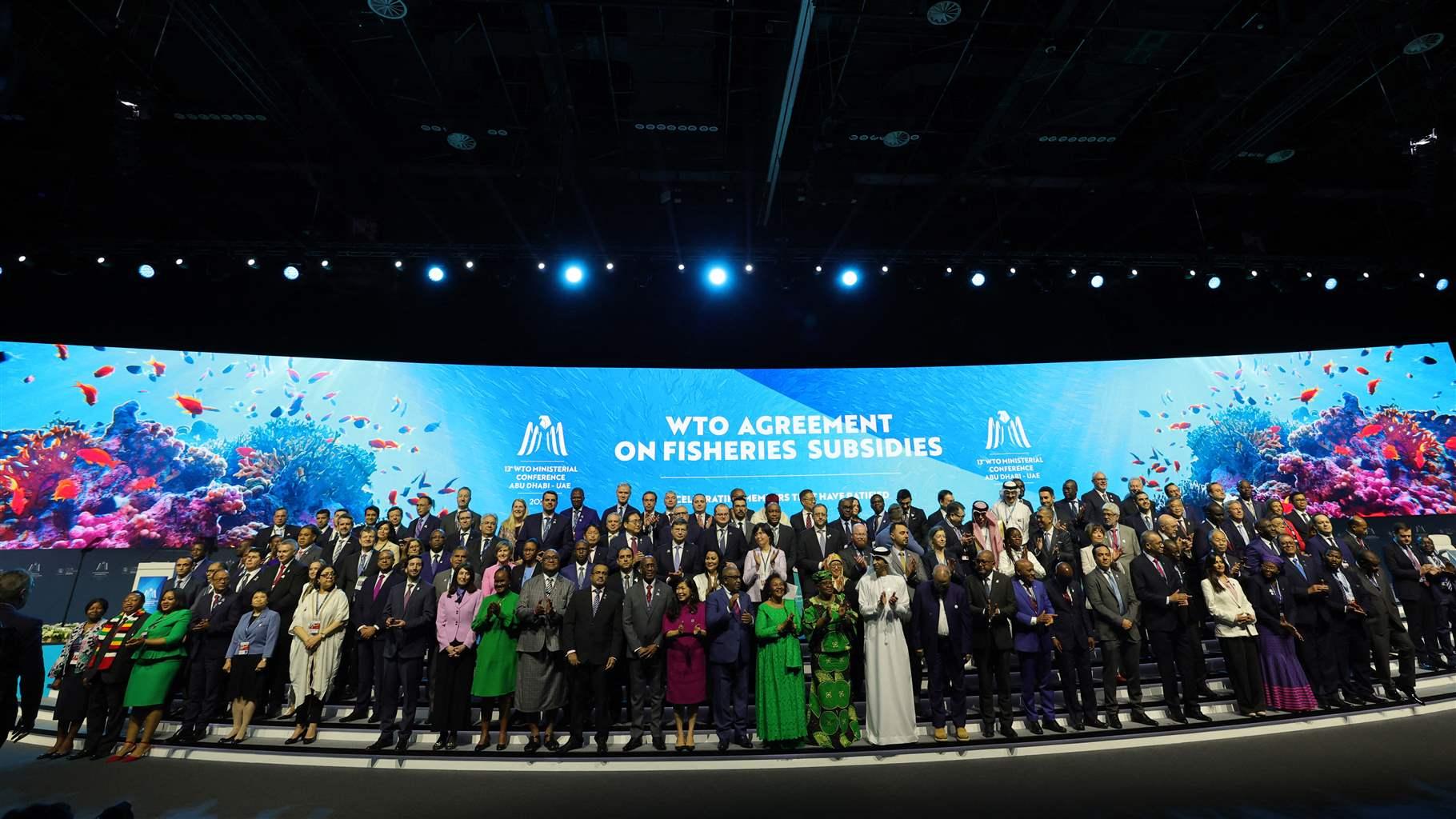

Last month, the World Trade Organization’s (WTO) 13th Ministerial Conference (MC13) tried to advance further rules to strengthen the existing Agreement on Fisheries Subsidies. That agreement, adopted by WTO members in June 2022 and still awaiting final ratification, prohibits subsidies that enable illegal fishing, fishing of overfished stocks and fishing of unmanaged stocks on the high seas. At the time, WTO members also agreed to work on additional provisions to limit subsidies that incentivize “overfishing and overcapacity” – the WTO’s term for a fleet’s ability to harvest more fish than is sustainable. These new rules would be important steps in addressing subsidies such as those that lower capital and operational costs, which in turn can encourage overfishing.
This year’s conference, in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, got off to a good start with nine further countries ratifying the 2022 agreement; a last-minute addition of South Africa at the end of the week brought the total to 71 members of the 110 needed for ratification. There were other early promising signs as well: Fiji put forth a strong proposal on behalf of the Pacific Group to increase the scope and ambition of the new rules to cap and reduce the harmful subsidies that big subsidizers provide to their fishing industry. This approach was not new, but members had found it difficult to reach agreement in previous negotiations. This time, members started to find compromises and to explore trade-offs to accommodate their concerns.
The draft rules designed to build on the 2022 agreement provided a good framework to improve countries’ accountability and address the problems of overfishing by domestic fishing fleets and distant-water fishing (in which countries fish beyond their own territories), with an emphasis on big subsidizers. The rules included a list of prohibited subsidies (for vessel construction and fuel, among others) and featured a strong management exception – calling for WTO members that provide a relatively higher level of subsidies to show that they have effective management measures in place to ensure healthy stocks in order to continue giving subsidies. The draft also included a requirement that members limit the subsidies for fishing beyond their own jurisdiction, including in a third country’s waters. And it included flexibility for developing countries to provide aid to artisanal fishers – and to their country’s industry in general – if their global contribution to marine capture, which is the harvesting of naturally occurring species in the ocean, is below 0.8%. A review clause was included to assess the effectiveness of the rules.
An agreement would have undoubtedly helped to improve ocean sustainability – and would have demonstrated that the WTO can deliver on other challenges of the global commons, such as climate change, food security and plastic pollution.
Unfortunately, despite extending the Ministerial Conference by a day and delaying the closing plenary several times, WTO members failed to reach consensus on new rules.
The repeated delays hint at how hard the chair of the negotiations and country delegations must have been working to finalize the text, trying to close gaps between competing asks and seeming to come tantalizingly close each time. But in the end, not all members could agree on the additional rules; this failure to prioritize sustainability is an oversight that will affect communities that rely on healthy fisheries.
And now?
WTO members are certainly not off the hook. The final rules are within reach, leaving members to renew their efforts to ratify the 2022 agreement so that it enters into force, and work hard to reach consensus on additional provisions that will help end all harmful fisheries subsidies as soon as possible. Fish stocks, coastal communities and the health of our ocean are counting on WTO members to do just that.
Ernesto Fernández Monge and Megan Jungwiwattanaporn work on cross-campaign efforts within The Pew Charitable Trusts’ conservation work.


America’s Overdose Crisis
Sign up for our five-email course explaining the overdose crisis in America, the state of treatment access, and ways to improve care
Sign up

WTO Members Agree to Help End Plastic Pollution


5 Rules Strengthen WTO Deal to End Harmful Fisheries Subsides