Shipping Vessel Noise May Affect Behavior, Availability of Arctic Cod
Pew marine fellows research shows changes in movement and behavior of important fish species

Historically, ice cover in the Arctic has acted as a natural barrier to shipping in the region. But as the changing climate warms oceans and reduces sea ice cover—September ice coverage in the Arctic in 2012 declined by an estimated 49 percent from the 1979-2000 baseline average—vessel activity is increasing. This boost in traffic is causing an associated increase in marine noise, which may be affecting the behavior and availability of key species.
A new study, published in January 2020 in Ecological Applications, found that underwater noise from anchored and moving vessels not only displaces Arctic cod (Boreogadus saida) to areas with less noise, but also alters their natural behaviors.
Because Arctic cod is a key species in Arctic marine ecosystems, any shifts in their distribution affects food availability for seabirds and marine mammals such as beluga whales (Delphinapterus leucas) and ringed seals (Pusa hispida)—which in turn could affect Indigenous communities in the Arctic that depend on marine mammals for subsistence hunting.
The study, whose co-authors include 2015 Pew marine fellows Aaron Fisk, professor at the Great Lakes Institute for Environmental Research at the University of Windsor, and Rob Williams, chief scientist at Oceans Initiative, is the first to address how Arctic fish species respond to vessel noise.
Food web effects on other animals
During August and September 2012, researchers used telemetry data to measure the effects of noise from stationary and moving ships on Arctic cod in Resolute Bay in Nunavut, Canada, with an emphasis on cod behaviors of searching, feeding, and traveling.
The researchers found that the fish responded to increased noise by moving away from the ships and aggregating in areas with deeper water. The fish also changed their swimming behaviors, by searching for food less and spending more time traveling. Based on these results, cod are believed to perceive vessel noise and presence as a threat—and to react by moving away and decreasing exploratory activities.
Because ships tend to operate near human communities, increasing vessel traffic may cause cod and other fish species to move farther away from these areas. In response, marine mammals may have to travel greater distances to forage for critical prey species, resulting in fewer marine mammals close to Inuit communities.
“Inuit food security may be affected if increasing ship traffic also disturbs Arctic cod near Inuit communities, contributing to exacerbation of an already existing food security issue,” said Silviya Ivanova, lead author of the study and Ph.D. student at the Great Lakes Institute for Environmental Research at University of Windsor.
Impacts of underwater sound
Fish use sound to forage, avoid predators, explore, navigate, and communicate. Vessel noise can make it harder for fish to hear predators and communicate with each other and can alter how they use their habitat.
The increase in vessel traffic, which includes cruise and cargo ships, is expected to continue in the Arctic, especially along the Northwest Passage—the shortest sea route between Europe and Asia. Shipping, including cruise ship traffic, has doubled in the Arctic in the past 20 years, and the number of days vessels spend in the Arctic has quadrupled. Acoustic noise in the Arctic marine environment is expected to continue to increase as well.
Understanding the shifts in cod behavior observed in this study, which could become more pronounced as vessel traffic grows, is important in the development of conservation and management approaches in the region as environmental conditions continue to change.
Polita Glynn directs the Pew Fellows Program in Marine Conservation.


America’s Overdose Crisis
Sign up for our five-email course explaining the overdose crisis in America, the state of treatment access, and ways to improve care
Sign up
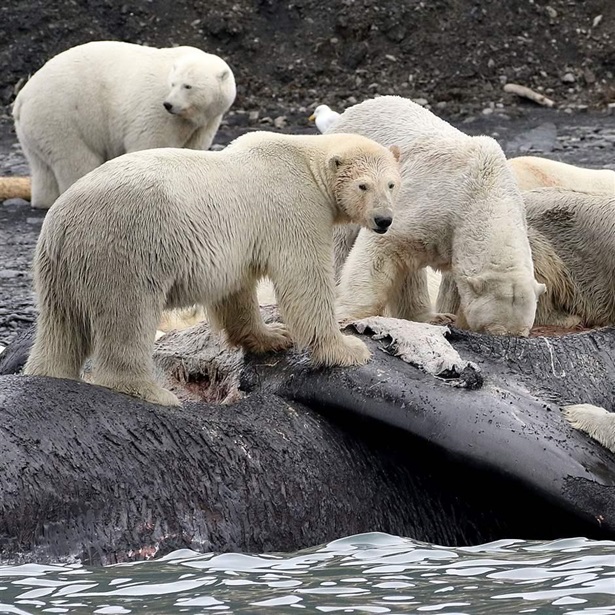

Dead Whales Can Help Polar Bears Survive Warming Periods but May Be Too Hard to Find