The Global FAD Science Symposium
Experts highlight ways to better manage a fishing gear frequently used to attract tuna
This page was updated on November 19, 2018 with new documentation for "Managing FAD Capacity and Impacts on Marine Ecosystems."
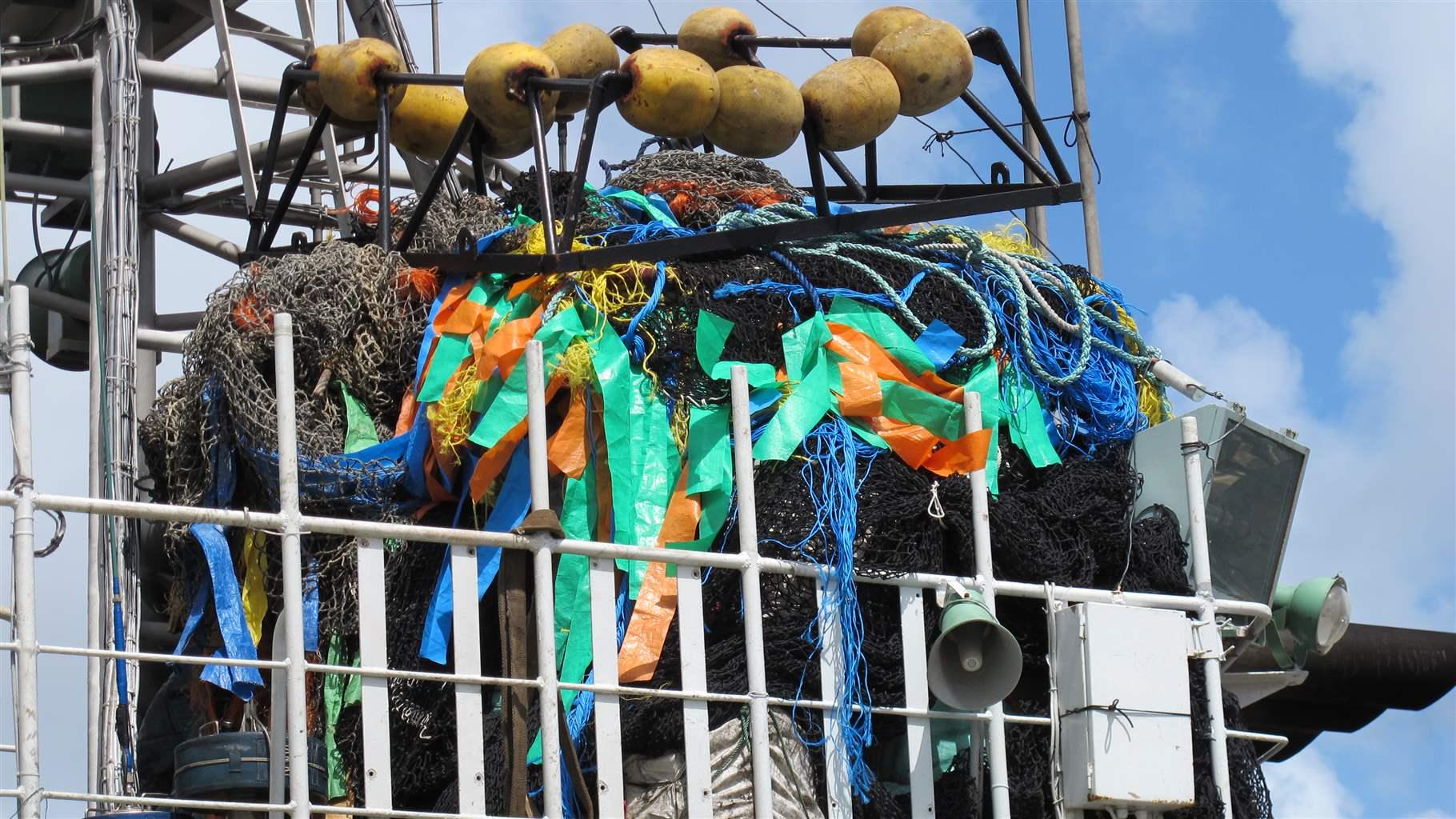
Purse seine fleets often depend on fish aggregating devices (FADs) to boost their efficiency in catching large amounts of skipjack tuna. But small or juvenile fish from two other tuna species—bigeye and yellowfin—can be caught at the same time, often before they have had a chance to reproduce. That then reduces the productivity and size of those stocks. FADs can also take a toll on other species and on marine and coastal environments. Sharks and turtles, for example, are attracted to FADs. They can become entangled in the large purse seine nets or the FADs themselves. And this gear is often abandoned at sea, where they contribute to marine debris.
FADs vary in design; some are anchored, while others are set adrift and equipped with tracking devices. They typically consist of a floating object, such as a raft, and webbing—often old netting or rope—that hangs in the water to a depth of 50 meters or more.
In recent decades, fishing fleets have increased their use of FADs, but the rules for deploying and fishing on them have not kept pace. Consequently, tuna fisheries scientists and managers have raised growing concerns about the gear. To address the issue, 31 scientists and other experts from around the world attended the Global FAD Science Symposium in Santa Monica, California, in March 2017, seeking to answer a fundamental question: What does well-managed FAD use look like within a tropical purse seine fishery?
Participants reviewed the latest scientific literature on FADs to assess their impact on the marine environment as well as the challenges associated with managing them. They then agreed on proven and promising strategies to mitigate the effects of growing FAD use. The experts also highlighted ways to improve the data and knowledge about FADs.
The points of agreement provided the basis for five papers intended to inform global FAD management. All participants signed the papers, which have been presented to the world’s regional fisheries management organizations as well as other audiences.
Below are links to the papers along with proceedings documents, including symposium presentation abstracts:
- Proceedings of the Global FAD Science Symposium
- Managing FAD Capacity and Impacts on Marine Ecosystems
- The Impacts of FAD Use on Non-Target Species
- FAD Use and Fishing Mortality in Tropical Tuna Fisheries
- Technological Approaches to Addressing Tuna Mortality Associated With FAD Fishing
- What Does Well-Managed FAD Use Look Like Within a Tropical Purse Seine Fishery?
Fisheries managers should consider the best practices spelled out in these papers and adopt strategies, as appropriate, to safeguard the health and sustainability of these fisheries and the greater marine ecosystem.