Nations Adopt Historic New Agreement for Nature
Convention on Biological Diversity framework aims to protect, conserve, and restore ecosystems by 2050

Following more than four years of negotiations, 196 countries agreed to a slate of actions and goals to safeguard biodiversity worldwide, including a key target to protect and conserve at least 30% of lands, inland water, and coastal and marine areas globally by 2030—also known as “30 by 30.” It is the largest area-based target ever agreed.
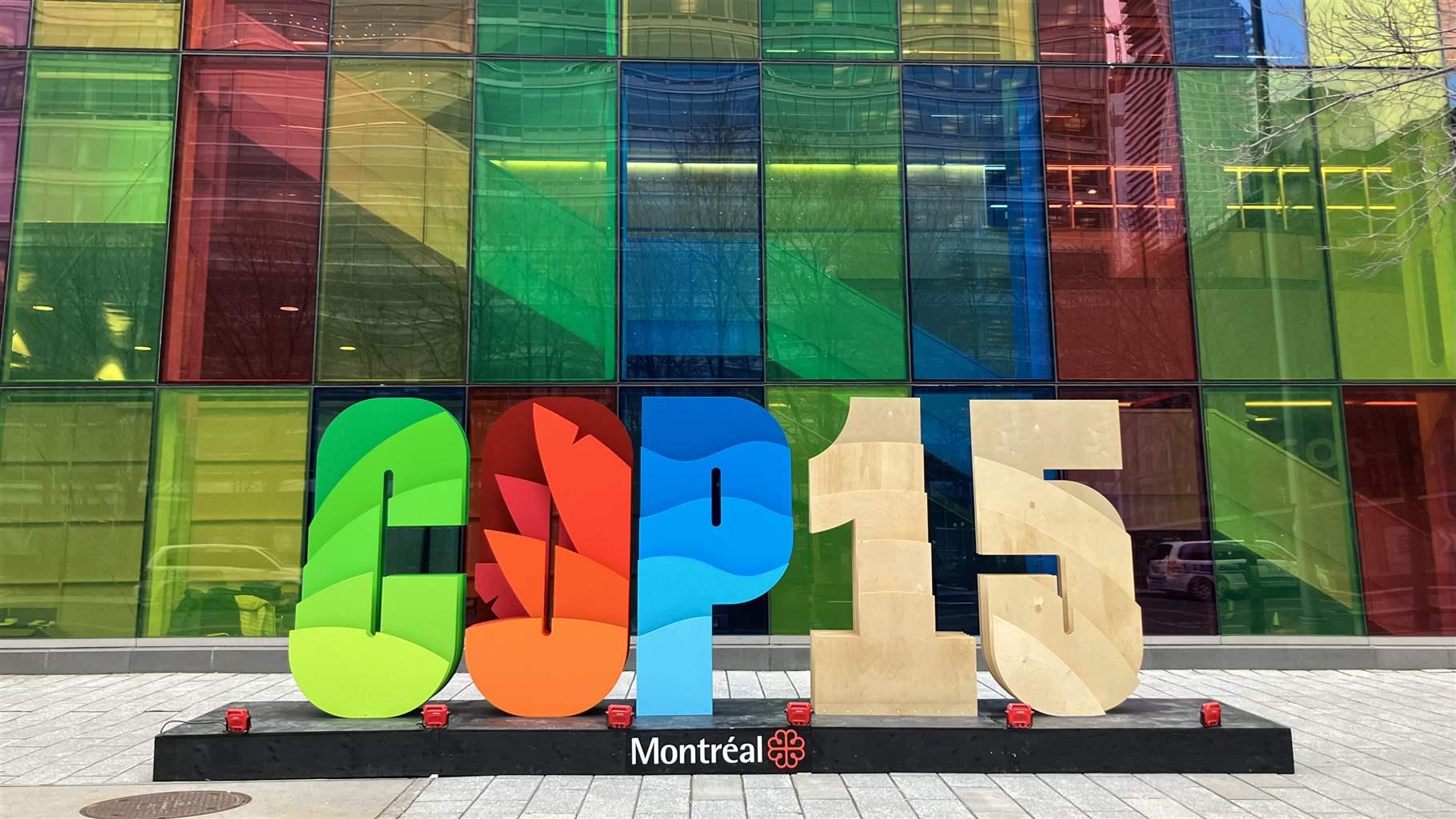
The adoption of the sweeping Global Biodiversity Framework came at the close of the 15th Conference of the Parties (COP 15) to the United Nations Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) and is, in the words of the CBD, a huge step toward a “world living in harmony with nature” by 2050. The agreement became official in the early hours of Dec. 19, when COP 15 President Huang Runqui, minister of environment and ecology for China, brought down the gavel to end the meeting.
The new plan, also referred to as the “Kunming-Montreal global biodiversity framework,” comprises four long-term goals to be achieved by 2050 and 23 action-oriented global targets for urgent action between now and 2030. Target 3—the 30 by 30 goal—is the most momentous; The Pew Charitable Trusts has advocated for this target since 2016 based on science showing the size and breadth of protections needed to ensure land and ocean sustainability, and research showing that protected areas must be governed by strict rules that yield the most benefits to biodiversity. The target supports this vision, calling for all 30 by 30 areas to be effectively conserved. It also reinforces the importance of “recognizing and respecting the rights of Indigenous peoples and local communities, including over their traditional territories.”
With the new framework, countries also committed to:
- Adopt an ecosystem approach to the harvest and use of wild species while respecting and protecting customary sustainable use by Indigenous peoples and local communities.
- Minimize the impact of climate change and ocean acidification through actions that include nature-based solutions.
- Prevent, reduce, and work towards elimination of plastic pollution.
- Sustainably manage their agriculture, aquaculture, fisheries, and forests.
- Eliminate, phase out, or reform incentives, including government subsidies, that harm biodiversity, and do so in a proportionate, just, fair, and equitable way.
- Maintain, enhance, and restore ecosystems, including by halting human-caused species extinction.
- Mobilize at least $30 billion per year to support global biodiversity conservation by 2030 by substantially and progressively increasing funding levels from where they are today.
- Ensure the full, equitable, inclusive, effective and gender-responsive representation and participation of Indigenous peoples and local communities in decision-making, information sharing, and other aspects of work related to biodiversity.
Looking forward, the focus for CBD countries is on delivering on the new Global Biodiversity Framework. Many countries, such as Australia and Chile, are leading the way by already protecting more than 30% of their lands and ocean. International bodies and governments have also taken action to end harmful fisheries subsidies, secure legal and sustainable fisheries, and reduce plastic waste on lands and into our streams, rivers, and ocean.
Pew is also committed to supporting country-led conservation efforts through our project work and partnerships such as Blue Nature Alliance, the Pew-Bertarelli Ocean Legacy Project, and Enduring Earth, the last of which will support projects announced at COP 15, including Indigenous-led conservation projects in Canada, as well as initiatives in Mongolia and Gabon.
Of course, delivering all the targets will not be easy. For one, governments and the global conservation community must secure the funding to close the gap between the money needed for conservation and what’s available today. This was a key point of discussion throughout COP 15. And all actions in the framework will need to be delivered through an approach that is inclusive and just. In this effort, Pew is working with Indigenous peoples, local communities, governments, scientists and academics, and funders to help ensure that all stewards of the environment are working to inform an inclusive path for conservation.
Despite the work ahead, this new agreement marks a historic moment. If leaders from all public and private sectors around the world can summon and sustain the political will, this framework should set our planet on a path towards recovery of all natural ecosystems and allow all people to, indeed, live in harmony with nature by 2050.
Masha Kalinina coordinates The Pew Charitable Trusts’ cross-campaign efforts with the United Nations Convention on Biological Diversity.