Arctic Oasis Sustains Northernmost Inuit Communities—and Marine Mammals
Protecting nutrient-rich North Water Polynya would help curb effects of changing climate

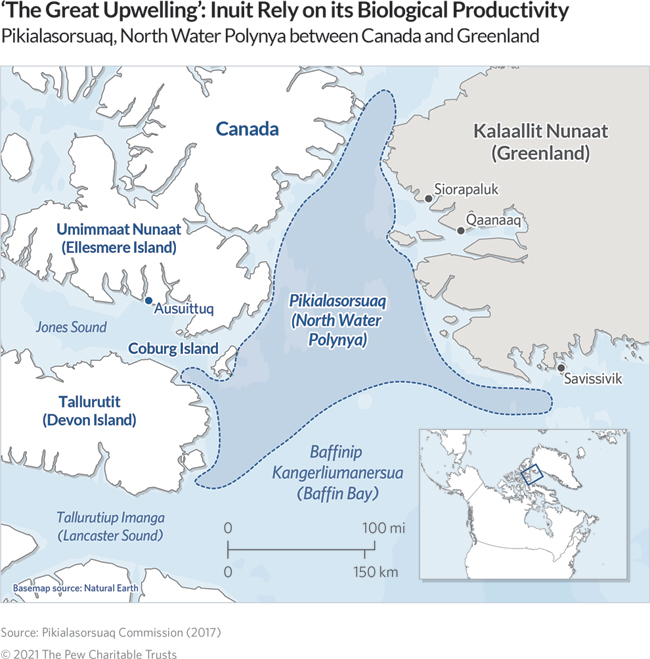
Between Canada and Greenland lies the most biologically productive ecosystem north of the Arctic Circle: an 85,000-square-kilometer (32,800-square-mile) region of ocean known in Greenland as Pikialasorsuaq (the Great Upwelling) and in Canada as Sarvarjuaq.
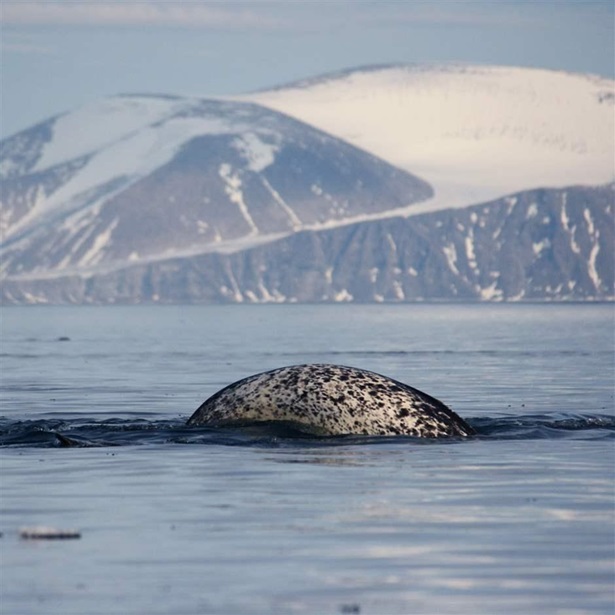
This marine oasis, which has sustained generations of Inuit hunters and fishers, is kept ice-free by upwellings of relatively warm waters from the Atlantic Ocean. Such open-water areas surrounded by sea ice are called polynyas. In Pikialasorsuaq/Sarvarjuaq, the upwelling allows for an early spring plankton bloom that provides nutrient-rich food for Arctic cod, a keystone species for the entire ecosystem. Large concentrations of marine mammals—including walruses, seals, and polar bears—feed on these cod, and the habitat is also a prime feeding area for millions of seabirds, including an estimated two-thirds of the world’s dovekies and thick-billed murres.
The formation of the polynya, which is one of the world’s largest, is dependent on the annual pileup of floating ice to its north, in Nares Strait. Here, sea ice moving southward from the High Arctic hits a bottleneck and forms a bridge between Greenland and Ellesmere Island, Canada, preventing ice from reaching the polynya. The ice bridge has been a human migration route for centuries and today still connects the Baffin communities of Canada and the Avannaata communities in northern Greenland—cultures that thrive on the polynya’s biological abundance. Because of climate change, the bridge is forming later each fall and breaking up earlier each spring, threatening the polynya and the stability of the greater Pikialasorsuaq/Sarvarjuaq system.
Since 2016, The Pew Charitable Trusts has supported Inuit in Greenland and Canada in their efforts to advance the Pikialasorsuaq Commission, an Inuit-led process to gather and record what Indigenous communities envision for the future of the polynya. This commission released recommendations in 2017, which include creating the first large international Indigenous Protected and Conserved Area, to be managed by Inuit, and connecting communities across the international boundary.
Peter Baker directs The Pew Charitable Trusts’ ocean conservation work in Canada and New England.