Anchovies—and Their Predators—Help Researcher Solve Ecosystem Mysteries
Aspiring ecologist's work off Florida's west coast could help inform fisheries policy
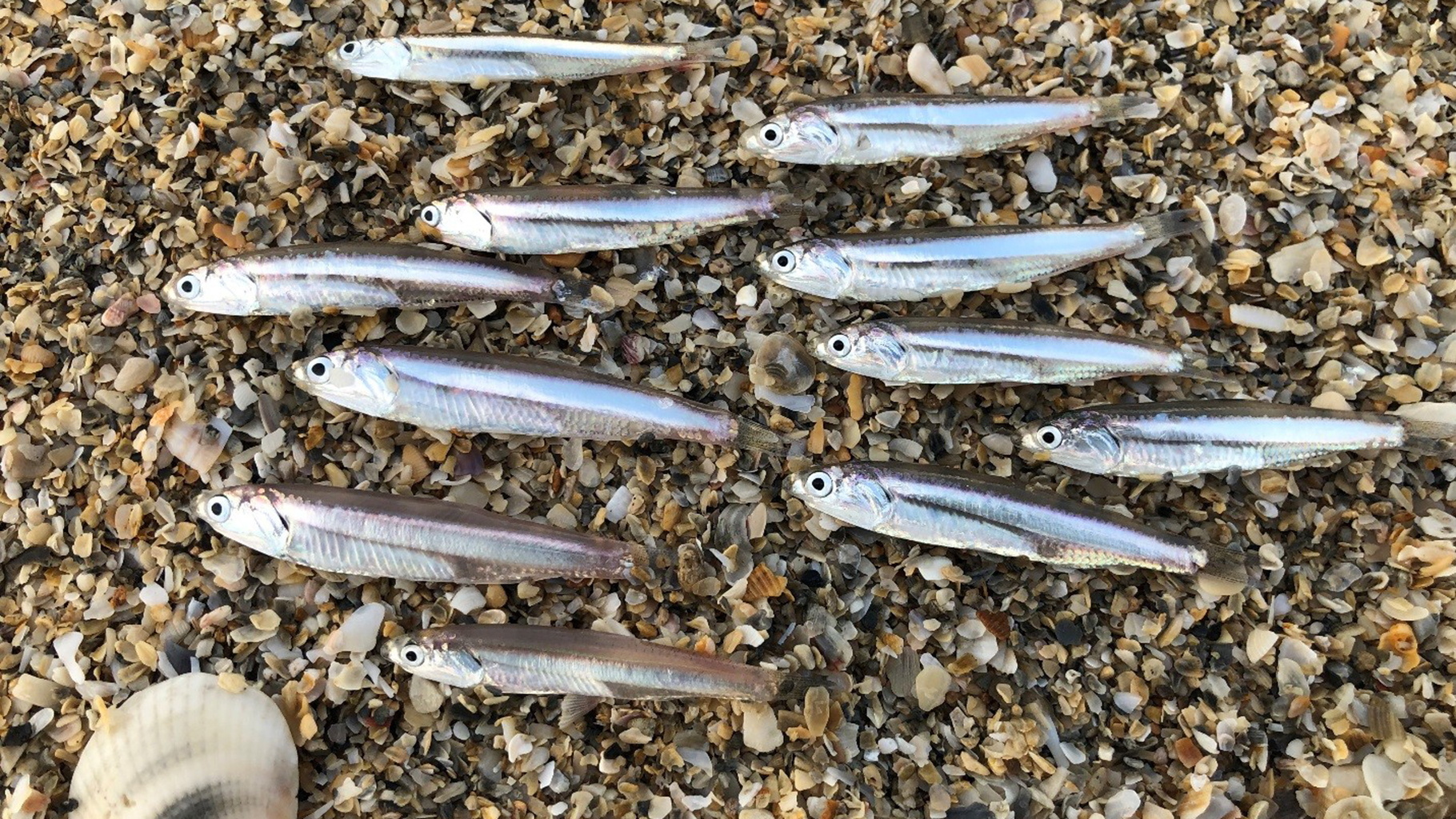

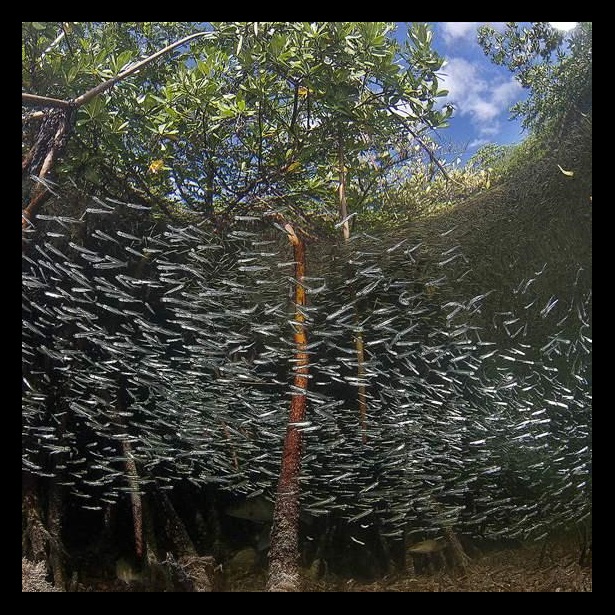
All anchovies may look similar to the untrained human eye, but that doesn’t mean they’re all headed for the same fate. Some end up as pizza toppings, some as bait, and some as food for larger fish, marine mammals, or seabirds.
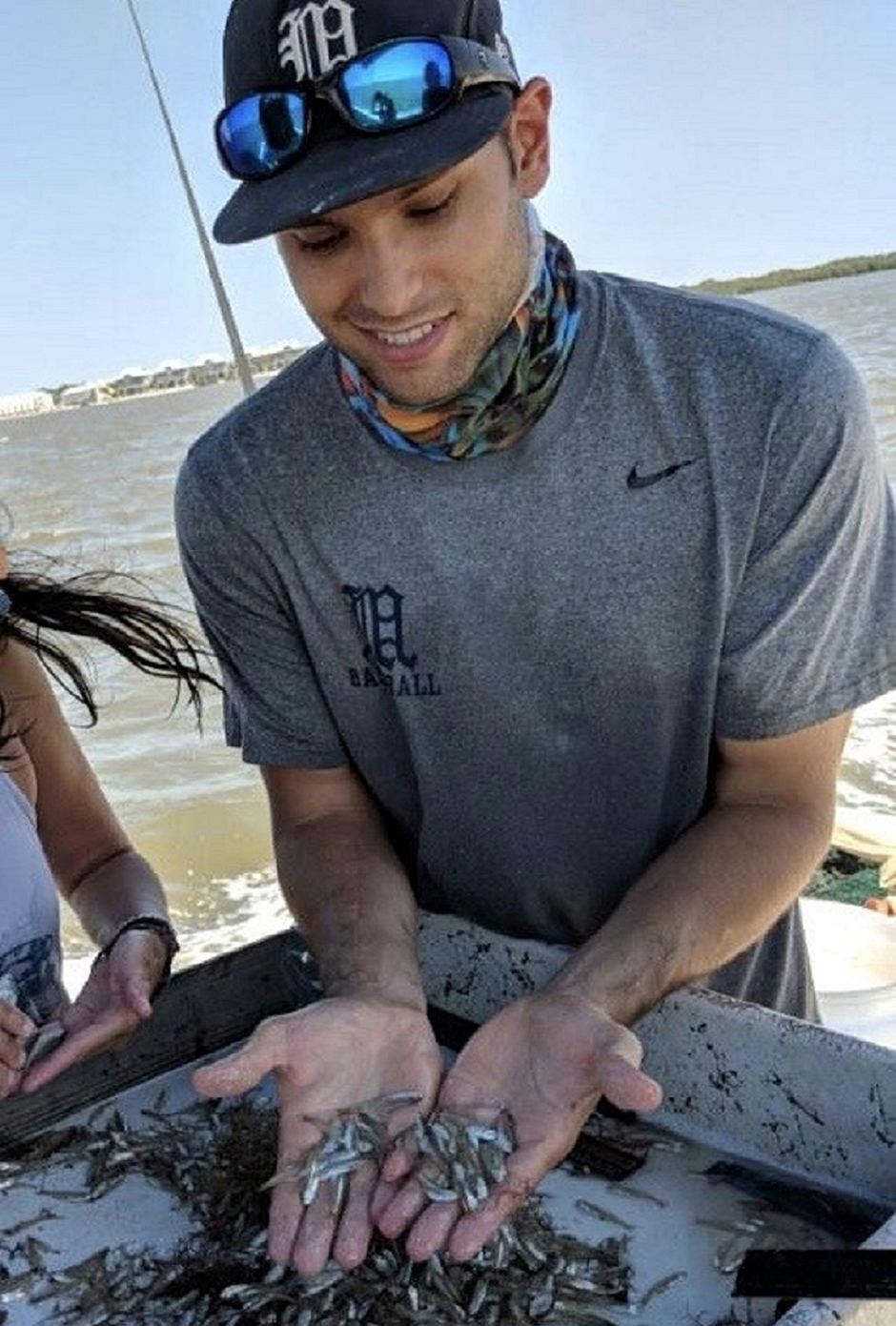
To Dylan Sinnickson, it’s that last category that matters most. The University of Florida fisheries and aquatic sciences Ph.D. student believes anchovies and the wildlife that eat them hold answers to how ecosystems work.
Sinnickson is studying how river flow affects bay anchovies and their predators at Cedar Key on Florida’s west coast. The region is known as the Nature Coast for its vast seagrass beds, salt marsh, and abundant wildlife that support fishing and other nature-based activities that form the backbone of local economies.
For the past year, the 28-year-old Sinnickson has been analyzing the impact of river discharge and the nutrients it brings to an estuary.
Sinnickson confirmed some basic things: More river water means the estuary provides added nutrients and food for marine life. Nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorous, cause an increase in plankton, which is food for anchovies. As anchovy populations grow rapidly, predators have more to eat.
But Sinnickson, using computer models and state fishery data from the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission, found there is much more to the story. In general, predators tend to enjoy an all-you-can-eat buffet only so long before they look for another food source. For example, Sinnickson’s modeling predicted that more anchovies would deliver bountiful meals for both snook and seatrout, giving their population numbers a boost. But snook benefited the most. With higher numbers, snook’s dietary needs grew, and they began preying more on another anchovy predator—seatrout.
“Most predatory fish species benefit from abundant prey, but it’s not a linear relationship,” said Sinnickson, who hopes to become a professor of fish ecology. “The ecosystem is complex and acts in unpredictable ways.”
The mysteries Sinnickson is unraveling are important because they can help fishery managers better understand complex food webs. If they can predict how or when some species may be abundant, they can set fishing rules accordingly.
Sinnickson’s investigation is part of the Forage Fish Research Program, which awards annual fellowships to students who study small prey species, also known as forage fish. The program is run by the Florida Forage Fish Coalition, which is led by the International Game Fish Association and includes The Pew Charitable Trusts, the Florida Wildlife Federation, the Angler Action Foundation, Wild Oceans, and the American Sportfishing Association. The coalition collaborates with leading academics and scientists from the Florida Fish and Wildlife Research Institute to increase knowledge about forage fish.
Estuaries host many kinds of forage fish and are breeding and feeding grounds for most of the larger fish that people like to catch. Flooding, runoff from land, and drought have major effects on estuaries, and Sinnickson’s research will help fishery managers take an ecosystemwide view of a place when making rules.
“People should care about changes and impacts to estuaries because ecotourism and fishing are some of Florida’s biggest industries,” said Sinnickson, who grew up fishing for striped bass with his parents on Long Island Sound. “We need information to sustainably manage these resources for future generations.”
Holly Binns directs The Pew Charitable Trusts’ U.S. Conserving Marine Life program in the Gulf of Mexico and U.S. Caribbean.