To Prepare for Flooding, New Jersey Town Helps Residents Relocate Out of Harm’s Way
Woodbridge Township grant manager says strategy grew from the destruction of Superstorm Sandy
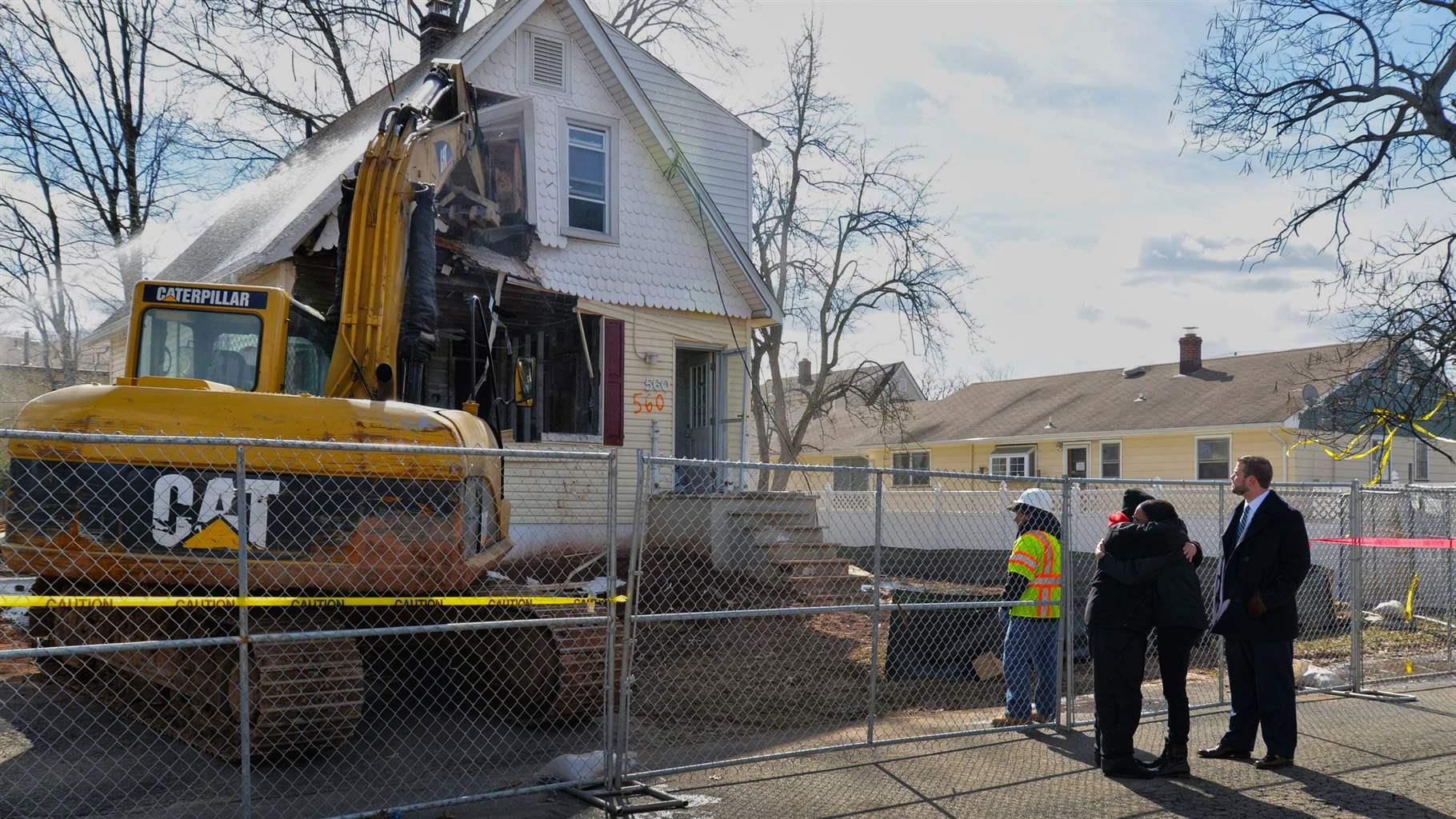

As grant manager in Woodbridge Township, New Jersey, Stacy Curry helps facilitate the use of incoming funds to best benefit residents. Curry has applied federal and state grants to help 166 families move out of flood-prone neighborhoods, which not only improved safety for those who relocated but also cut the costs of future flooding for the state government and the town.
The Pew Charitable Trusts spoke with Curry about how local governments can leverage state and federal programs to lower flood risk in their communities. Curry’s responses have been edited for clarity and length.
Q: New Jersey is one of the most densely populated states in the U.S. What actions has Woodbridge taken to help relocate people from high flood-risk areas?
A: Woodbridge has a voluntary program, so homeowners are free to choose where they want to relocate. If the homeowner wants help relocating, the town and state will provide that. The town will reach out to housing developments with waitlists to see if they can prioritize relocated residents. The state has also helped by providing realtor-like services—for example, working with residents to help them find what they’re looking for. On the buying side, the state purchases high-risk properties with grant funds, and a deed restriction ensures that it won’t be developed. Woodbridge has also rezoned the area to prevent any future development. Importantly, neither residents nor developers opposed the rezoning effort, showing the town’s appetite for reducing risk.
Q: How did Hurricane Sandy affect how Woodbridge approaches flood mitigation efforts such as buyout programs?
A: Woodbridge did not have a buyout program until after Hurricane Sandy in 2012. Following Hurricane Irene in 2011 and then Sandy, we realized homeowners in flood-risk areas needed some form of relief, so we began to participate in Blue Acres, the state’s program focused on buyouts. Following Sandy, the town also passed an ordinance to rezone the flood-prone area to prevent future development or improvements to existing properties without mitigation. Fewer properties within flood plains means less flood damage during future events. The ordinance also identifies building design standards for existing structures to include mitigation or elevation, which meet the Federal Emergency Management Agency’s standards and are triggered by any proposed demolition, addition, reconstruction, or renovation to an existing structure. It requires the same standards upon change of ownership/tenancy and prevents new construction within the flood zone.
Q: How do you work with nonprofits and other stakeholder groups to build support for buyouts in communities?
A: We enlisted the help of a few nonprofit groups such as The Land Conservancy, Middlesex County Long Term Recovery Group, and Catholic Charities. They were key in reaching out to residents, identifying additional funding sources, and helping residents with relocations, land preservation, and rehabilitation, for example by telling residents their options and steering them to resources they—and we—may not have known about. The Land Conservancy Group was especially supportive in helping residents complete applications and providing interpreters for residents with language barriers.
And the Middlesex County Long Term Recovery Group was created to help residents with funding from donations, grants, and organizations such as Catholic Charities for costs related to attorney fees, rental assistance, moving, and storage units.
Q: How have federal recovery initiatives and state programs such as Blue Acres influenced the town’s efforts to relocate residents from flood-prone properties?
A: The Blue Acres program made it possible for the town to offer residents relief from flooding. In addition to administering the program, the state had funding from federal programs. It was up to the resident to voluntarily apply and choose where they were going to relocate.
Q: What can other communities—in New Jersey and beyond—learn from your experiences that might help them decrease people’s flood risk?
A: Our efforts were in response to disasters. I think it is important for communities to plan ahead and identify the risks prior to an event, then plan to mitigate before the event occurs. Local communities can take actions such as implementing local ordinances that restrict building or improvements in a flood zone without mitigation. Communities should also consider moving forward with rezoning efforts, elevating properties out of harm’s way, and retreating to the extent possible before it’s too late.