Dam Removal in Washington State Promises to Benefit Fish, Whales, and People
Government decision to restore free-flowing Nooksack River follows collaborative, science-based effort
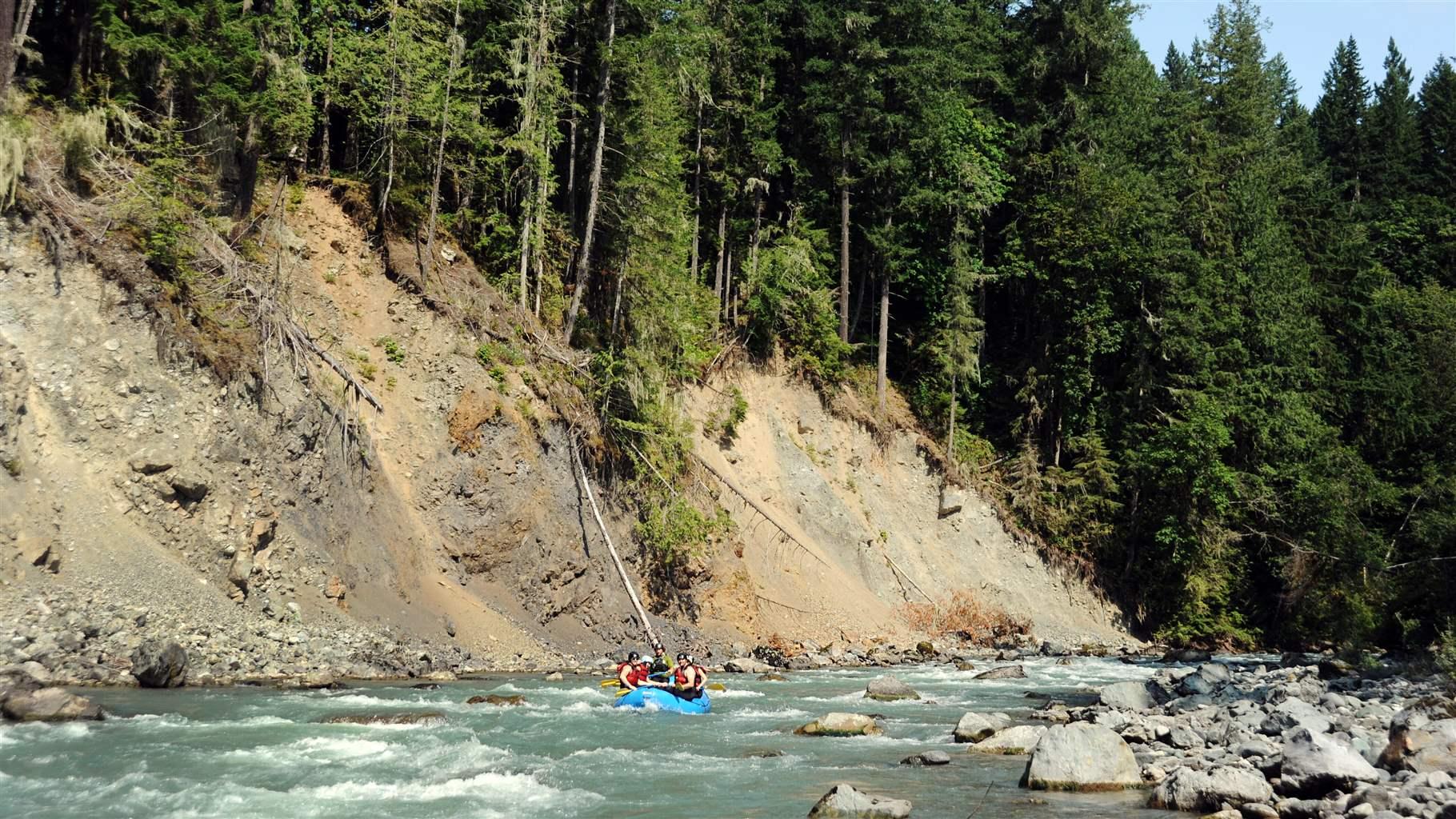

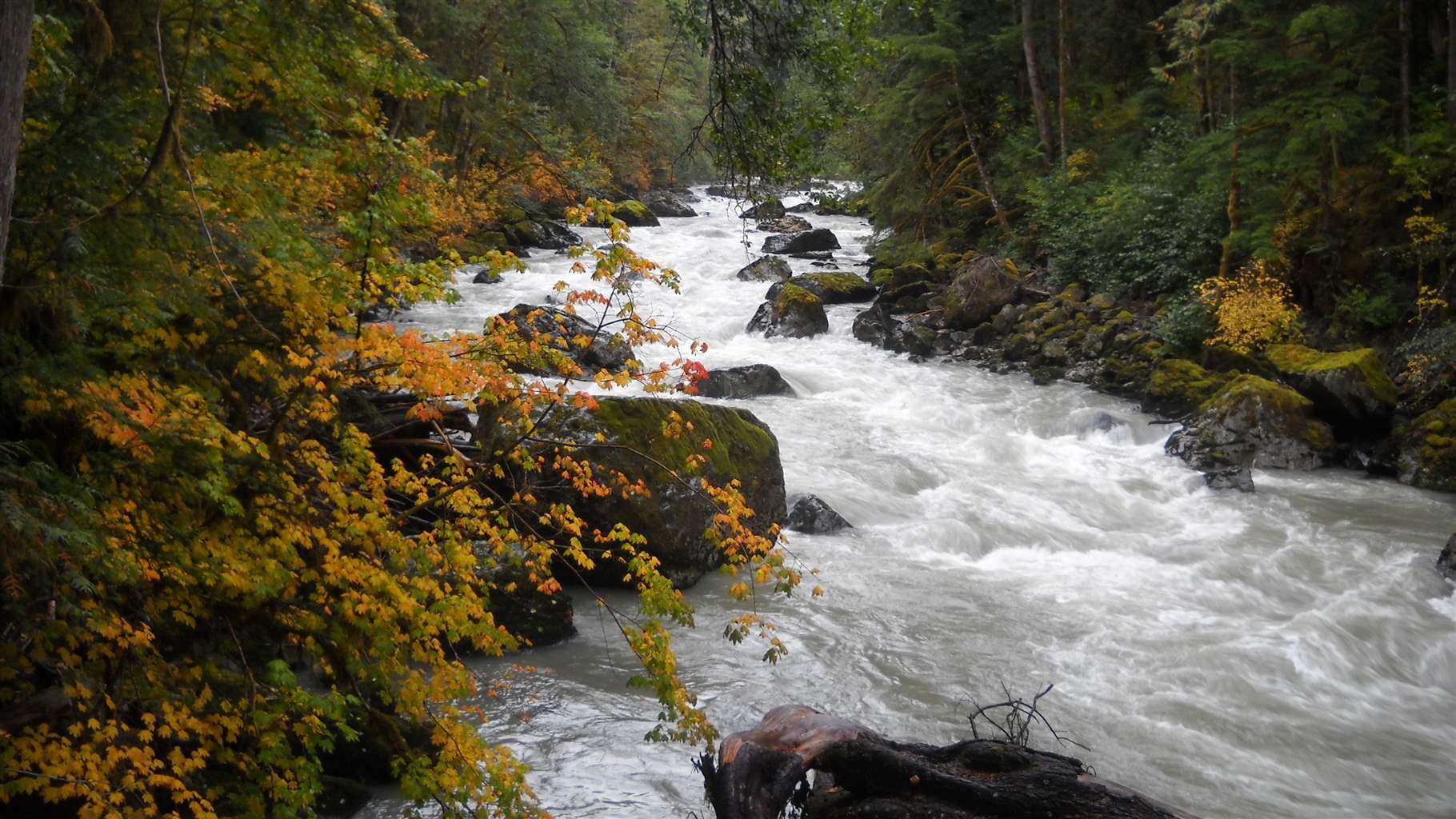
The Middle Fork Nooksack River originates on the southern slope of Mount Baker in northwestern Washington, flows northwest through the Cascade Range and the Mount Baker Wilderness, and joins with the Nooksack’s north and south forks before emptying into the Pacific Ocean. Along the way, the river runs through agricultural lands and the city of Bellingham, where it’s a source of clean drinking water for residents.
The river holds spiritual and cultural significance to local Indian nations, including the Nooksack Indian Tribe and the Lummi Nation, which for millennia have used the Nooksack valley for hunting, foraging, and religious activities. The Middle Fork Nooksack River is also home to salmon and steelhead trout, an important resource for the tribes. In 1855, both tribes signed the Treaty of Point Elliott, under which they exchanged land for the right to forever fish, hunt, and gather in the Nooksack River watershed.
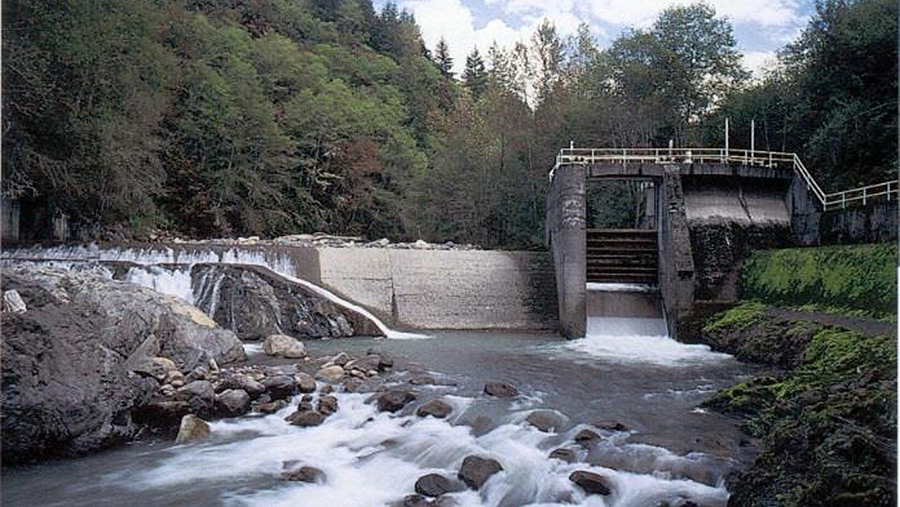
However, in 1961, the city of Bellingham constructed the Middle Fork Nooksack River Dam, some 20 miles upstream from the river mouth, to divert drinking water for the city. The dam stands approximately 30 feet high and 150 feet long and completely blocked salmon and steelhead migration, cutting off the spawning and rearing habitat for three anadromous species, all of which are endangered—Puget Sound Chinook salmon, steelhead trout, and bull trout—as well as other native species. The loss of salmon caused by the dam also adversely affects many tribal ceremonies and traditions, such as the annual First Salmon ceremony. Fisheries in the river have dipped to dangerously low numbers, and water quality has also been reduced. These impacts are felt by both people and wildlife, signaling that it’s time for the dam to go.
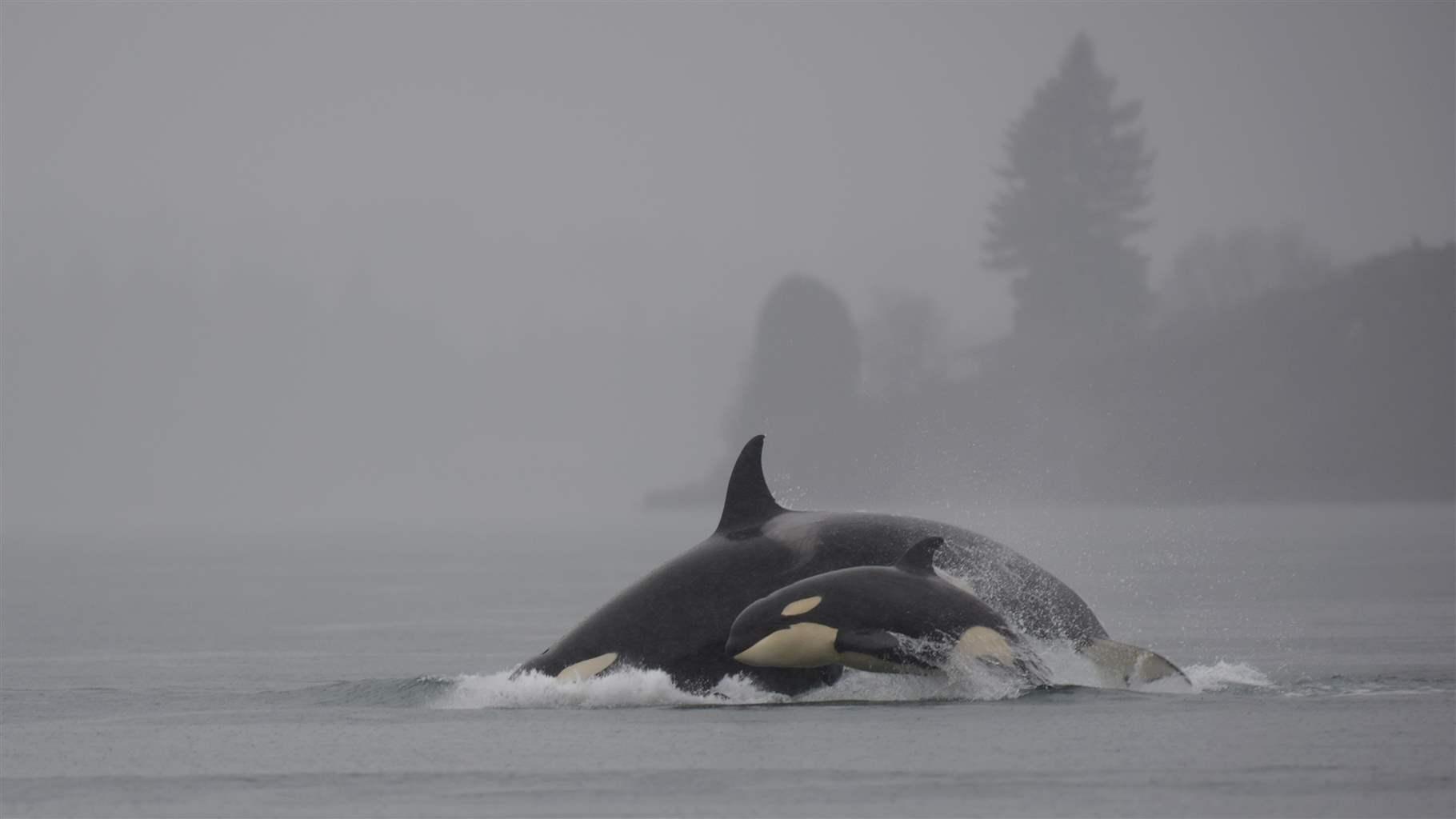
Puget Sound orcas, for example, are listed as endangered in large part because of a lack of salmon. Today, just 73 of these mammals remain—the lowest number in more than 30 years. According to the Center for Whale Research, approximately 75% of newborns in the past 20 years have died, and 100% of the pregnancies in the past three years have failed to produce viable offspring. Scientists believe these reproductive failures are due in part to the lack of available Chinook salmon, which represent at least 80% of a Puget Sound orca’s diet. To survive, the orcas need more salmon than Washington rivers are currently producing, and salmon need clean, cool, free-flowing rivers to rebound.
In response to this dire situation, Washington Governor Jay Inslee issued an executive order requiring state agencies to take immediate actions to protect Puget Sound’s southern resident orcas. His order established the Southern Resident Orca Task Force consisting of nearly 50 members representing a wide range of sectors, including state agencies, the Legislature, and state, tribal, federal and local governments, as well as private sector and nonprofit organizations. On Nov. 24, 2018, the task force released its recommendations for restoring Puget Sound orca, including removal of the Middle Fork Nooksack Dam.
Removal of the dam is also the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA’s) top recommended action to help Puget Sound Chinook salmon recover. Dam removal has the potential to increase Chinook salmon populations by more than 30%, according to NOAA.
Years of work by a coalition of state and city representatives, conservation groups including American Rivers, and the Nooksack Indian Tribe and Lummi Nation to craft a plan to remove the obsolete dam are paying off. This summer, the city will begin the months-long process of removing the physical structure and restoring a free-flowing Middle Fork Nooksack River. The project will provide fish with access to more than 16 miles of the river above the dam and open up more than 350 miles of fish spawning and rearing habitat in the watershed.
Restoring the Nooksack River to its free-flowing state will benefit wildlife, ecosystems, and people—from native tribes and residents of communities that need clean drinking to anglers and whitewater boaters who will have new sections of river to explore for the first time in 60 years. Hopefully the success of this collaborative project will serve as a model for other states and communities seeking to craft a better future by undoing mistakes of the past.
Nicole Cordan is a project director with The Pew Charitable Trusts’ U.S. public lands and rivers conservation program.