New Federal Policy Advances Nature-Based Protections for Property and Habitat
Army Corps move recognizes that living shorelines are a viable alternative to hard-built infrastructure
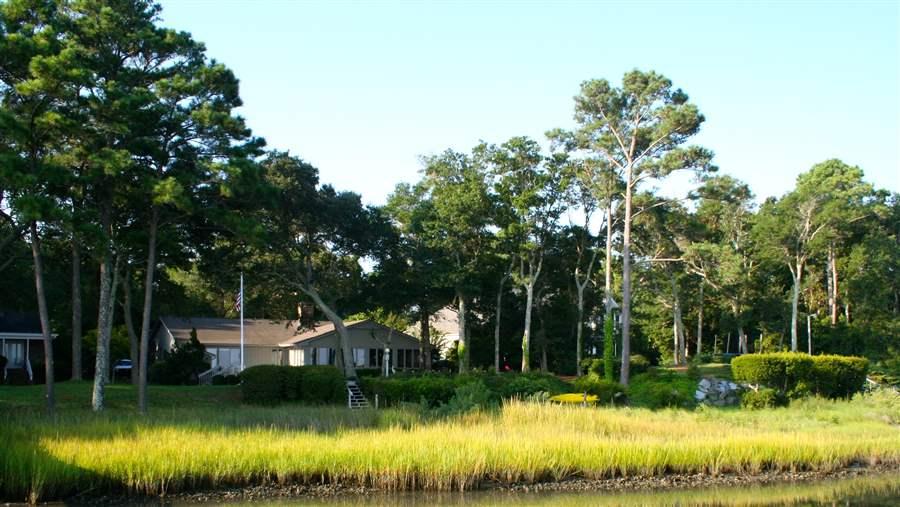

This tidal fringing salt marsh—an example of a living shoreline protective barrier—in Pine Knoll Shores, North Carolina, helps control erosion.
© Rachel Gittman
In a major step toward better protecting coastlines, estuaries, and lakeshores, the Army Corps of Engineers eased the permitting process, effective March 19, 2017, for living shoreline projects—those that use natural and nature-based defenses against storm damage and erosion.
Living shorelines—typically consisting of native elements including vegetation, oyster reefs, or rock sills—have proved effective in providing such protections when compared with hard infrastructure, like seawalls and bulkheads. The new Corps policy will reduce the time and cost associated with gaining a permit, encouraging more property owners to use living shorelines.
Pew-supported research found that living shorelines foster more biodiversity than do seawalls. Further, “hard” barriers often lead to the loss of wetlands and other natural habitats; some 14 percent of the U.S. coastline is already hardened.
A bipartisan group of elected officials, including members of Congress, state legislators, and local government representatives, supported the new permitting policy.
Many states are already seeing the benefits of living shorelines. North Carolina is using rock sill, oyster reefs, and marsh vegetation to successfully protect valuable habitat. And projects in Alabama and Texas are using nature-based techniques to combat erosion along the Gulf of Mexico.
The new permit process removes major barriers to implementing living shorelines projects across the country and puts the approval process for nature-based solutions on a par with permitting for hard infrastructure. That’s a big win for property owners, communities, and the countless species that thrive in the natural environment.
Laura Lightbody directs The Pew Charitable Trusts’ flood-prepared communities project.