Riverside Polytechnic High School
Riverside, California
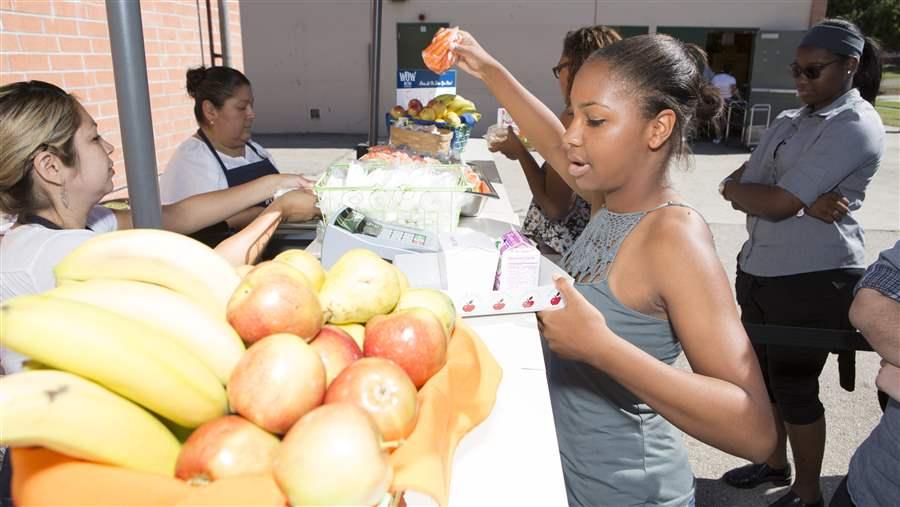
Officials in the Riverside Unified School District know that efficient service and a fun atmosphere can go a long way toward engaging students, especially at lunchtime. The district’s meal program has been a nationally recognized leader in serving healthy, delicious foods since pioneering the farm-to-school salad bar in 1997. At Polytechnic High School, lunches include fresh, colorful salad options that are so popular, they sell out every day; healthier versions of traditional favorites such as chicken and waffles; and an outdoor barbecue station that offers mouthwatering entrees, including rib sandwiches and chicken on the bone. But members of the nutrition staff at Polytechnic don’t rest on past achievements; they are always seeking ways to improve the meals they serve to the school’s 2,700 students. To that end, the school applied for a U.S. Department of Agriculture grant for three pieces of equipment to increase storage capacity, food quality, and service.
To ensure that students have time to eat those delicious meals, Polytechnic set a goal of keeping kids’ wait times in the cafeteria to seven minutes or less, an ambitious target for a campus with thousands of teens, one indoor serving line, and a handful of outdoor concession-style stations. To help meet this lofty goal, Polytechnic used part of its USDA grant to add a mobile cart equipped with an audio system.
“Kids love going to the mobile cart. It plays music and offers the students another location to get the foods they want,” says Joanne Hollingsworth, site manager.
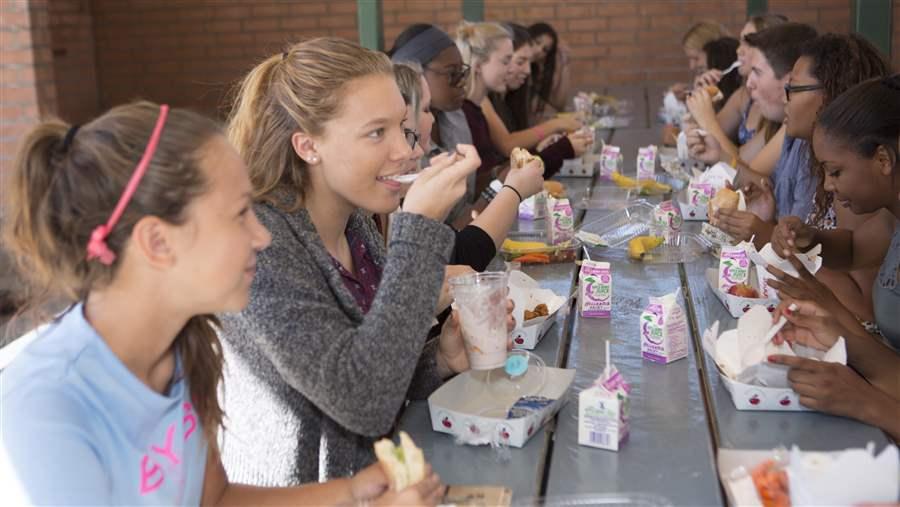
Students who used to skip school meals because of long waits are now able to visit the mobile cart to get lunch fast. Since the cart’s introduction, the school is serving an additional 100 lunches a day, bringing the daily total to more than 1,000. This increase would be impressive at any school, but at Polytechnic, where students are offered more choices than at many restaurant chains (five to six types of fresh salads, at least five entrees, and an array of barbecue options), this is quite a feat.
While the cart shortens waits, the second portion of the grant funds was used to increase meal quality. A 16-year-old ice machine was replaced so the school could have a reliable tool to chill milk, juices, and fresh items on the mobile cart and in serving lines.
“Salad bars aren’t as popular at the high school as they are in the younger grades. High school kids often choose prepacked salads instead, to decrease the amount of time they spend waiting in line,” says Kirsten Rolosen, the district’s assistant nutrition services director. “We know food displayed on ice sells better, so having an ice machine that works is important.”
For years, the district has led the way in forging new strategies to encourage healthy eating. It’s also built strong partnerships with local farmers to ensure that the meal program has plenty of fresh, local items. Polytechnic bought a three-door freezer with the third portion of the USDA funds to expand storage capacity and improve energy efficiency. Compared with the old, two-door unit, the new freezer has 33 percent more space, which allows the district to buy more of the farm-fresh items in bulk at peak nutrition and frees up staff time coordinating deliveries.
As Christine Fonseca, the cafeteria supervisor, says, “Temperatures in the kitchen often exceed 100 degrees, so having proper storage equipment is essential for the safety and life span of the foods.”



America’s Overdose Crisis
Sign up for our five-email course explaining the overdose crisis in America, the state of treatment access, and ways to improve care
Sign up
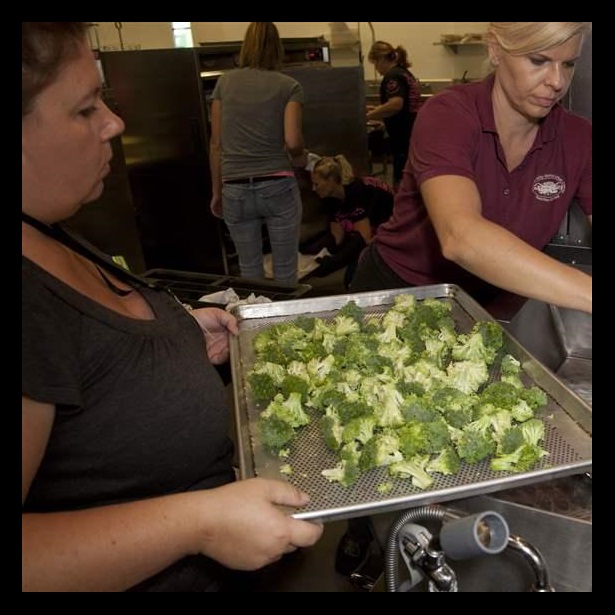

USDA’s School Kitchen Grants Benefit Meal Programs and Students
The right equipment makes a difference in efficient...
Learn More

School Nutrition Gets a Boost From USDA Kitchen Equipment Grants
School Nutrition Gets a Boost From USDA Kitchen Equipment Grants
Learn More