Driving to 54.5 MPG
The History of Fuel Economy
A timeline on the history of fuel economy in the United States.
2000-Present
“This will be win, win, win; it will reduce reliance on oil, strengthen energy security and mitigate climate change.”
— Transportation Secretary Ray LaHood, referring to the proposed CAFE standards, 2010
-
Light duty vehicle proposed rule: In November 2011, the EPA and NHTSA issued a proposed rule that would increase joint fuel efficient and tailpipe emission standards to a fleet average of 54.5 miles per gallon by model year 2025. The proposed rule received broad support from automobile manufacturers, national manufacturers, organized labor, environmental advocates, and national security organizations.
-
Medium and heavy duty vehicle final rule: In August 2011, the EPA and NHTSA announced the final joint fuel efficiency and tailpipe emission standards for heavy duty vehicles. The new rule covers model year 2014-2018 heavy duty vehicles in three groups – combination tractors, heavy-duty pickup trucks and vans, and certain vocational vehicles. This standard will save vehicle owners and operators $50 billion in fuel costs, reduce oil consumption by 530 million barrels, and decrease carbon pollution emissions by 270 million metric tons over the life of vehicles produced in the 2014-2018 model years.
-
Medium and heavy duty vehicle draft rule: In October 2010, the administration proposed the first joint fuel efficiency and tailpipe emission standard for medium and heavy duty trucks. Transportation accounts for 72 percent of oil consumption in the United States, and heavy-duty vehicles are the fastest growing segment within the transportation sector.
-
In October 2010, the administration proposed a CAFE standard for medium- and heavy-duty trucks. The program is projected to save 500 million barrels of oil and 250 million metric tons of carbon dioxide emissions in the first five years. Covered vehicles would be separated by type and fuel, with fuel-economy improvements of 20 percent for combination tractors, 10 percent for gasoline trucks and vans, and 10 percent for diesel trucks and vans and all vocational vehicles (such as dump trucks and cement mixers) by model year 2018.
-
In April 2009, President Barack Obama accelerated the increase in the previous administration's CAFE standards. The joint Environmental Protection Agency/NHTSA rule applies to model years 2012 to 2016, requiring a fleet-wide average of 35.5 mpg by 2016. Increasing at an average of 5 percent annually, most passenger cars must achieve 39 mpg, and light trucks 30 mpg, by 2016. Accompanying this announcement was a memo expressing the intent to create emissions standards for medium- and heavy-duty trucks, as required by the 2007 EISA.
-
In December 2007, Congress passed the first changes to U.S. fuel-economy standards in nearly 20 years. A part of the larger Energy Independence and Security Act (EISA) of 2007, the provision raised CAFE standards for cars, SUVs and pickups by about 40 percent—to 35 mpg by 2020.
-
The 2006 light-truck rule replaced the single average standard for each automaker's light-truck fleet with a size-based system that tied mileage requirements to a vehicle's footprint.
-
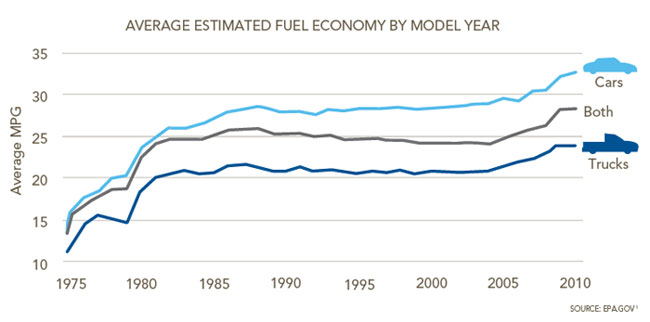
After Congress lifted the freeze on fuel economy in 2000, the administration enacted a pair of minimal light-truck increases. The most stringent of these, finalized in 2006, is to raise standards from 22.2 mpg to 24 between model years 2008 and 2011, an annual increase of 2 percent.
-
In 2002, the National Academy of Sciences reported that cars and trucks could meet a 37-mpg fleet-wide standard within 10 to 15 years without sacrificing performance or safety. The group also estimated that the nation was saving 2.7 million barrels of gasoline a day because of previous increases in vehicle efficiency.
“Cost-efficient fuel economy increases of 12 to 27 percent for cars and 25 to 42 percent for light trucks were estimated to be possible without any loss of performance characteristics ... [or] degradation of safety.”
— National Academy of Sciences, 2002
1990s
"There's no better argument for reducing our dependence on foreign oil than news reports from the Persian Gulf."
— Sen. Richard Bryan, fuel-economy bill co-sponsor, March 1991
-
The steady increase in light-truck sales, largely due to lower fuel-economy standards for trucks and SUVs, actually drove down fleet-wide efficiency during the 1990s. The average car and truck sold at the end of the decade went about a mile less per gallon of gas than 10 years earlier.
-
When the Clinton administration began the process for raising light-truck fuel economy standards, Congress responded with an appropriations rider taking away the administration's authority to increase vehicle efficiency. This anti-fuel economy rider remained in effect from 1995 to 2000.
-
In 1990, Sens. Richard Bryan (D-Nev.) and Slade Gorton (R-Wash.) sponsored legislation that would raise fuel-economy standards for cars and light trucks 40 percent over a decade. It was passed by the commerce committee but was filibustered on the Senate floor. Had it passed, the United States would now be saving more than a million barrels of oil per day.
1980s
-
Vehicle efficiency increased steadily throughout the early 1980s as the fuel economy law of 1975 was phased in.
-
Between 1975 and 1985, average passenger vehicle mileage doubled from about 13.5 mpg to 27.5, while fuel economy for light trucks increased from 11.6 mpg to 19.5.
-
In the mid-1980s, however, Ford and General Motors lobbied the Reagan administration to lower the standard. NHTSA complied, setting a 26-mpg standard for 1986, prompting Chrysler Chairman Lee Iacocca to declare, “We are about to put up a tombstone: ‘Here lies America's energy policy.'”
-
At industry's urging, NHTSA kept fuel-economy levels for at 26 mpg, below the benchmark set by Congress. The agency also failed to raise light-truck standards during this period, holding them at 20.5 mpg. Finally, in 1989, NHTSA restored the 27.5-mpg passenger-vehicle standard but lowered light-truck requirements to 20 mpg.
1970s
"CAFE protects American jobs. If CAFE is weakened now, come the next energy crunch American manufacturers will not be able to meet the demand for fuel-efficient cars."
— Chrysler advertisement, New York Times, Aug 11, 1985
-
In response to the oil price shocks of the early 1970s, Congress passed the nation's first Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) standards in 1975. The law called for a doubling of passenger-vehicle efficiency—to 27.5 miles per gallon (mpg)—within 10 years. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) was also given the authority to set a separate standard for “light trucks,” which accounted for a fifth of new vehicle sales at the time. By 2002, light trucks had surpassed cars as the leader in light-duty vehicle sales.
-
That fuel economy law gave NHTSA the authority to propose standards beyond 27.5 mpg for passenger vehicles, subject to veto by the Senate.
-
Domestic automakers predicted that fuel economy improvements would require a fleet primarily of subcompacts. In 1974, a Ford executive testified that the standards could “result in a Ford product line consisting . . . of all sub- Pinto-sized vehicles.” Despite these objections, Congress passed the law, and Ford's top seller today is its F-Series pickup.