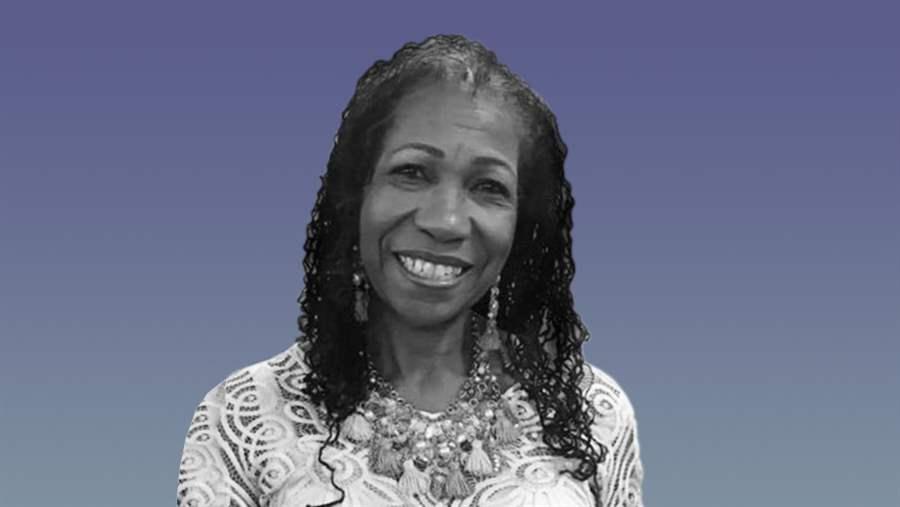
Why Faith Leaders Are Talking About Dying: A Q&A With Gwendolyn Phillips Coates
Discussing end-of-life issues can help families make care decisions their loved ones would want
First in a series
Since her husband’s sudden death in 2001, Gwendolyn Phillips Coates has devoted herself to educating others, especially African-Americans and those in underserved communities, about end-of-life planning. Among her many roles, she has served as a pastor at Providence Hospice of Seattle and as its diversity director and outreach coordinator. She has also written a book about her experiences with grief.
More recently, she has worked as the community liaison with physician Maisha Robinson in a pilot program to promote advance care planning for elderly African-Americans through Los Angeles churches. Coates, who lives in California, is the founder and pastor of God Answers Prayer International Fellowship of Churches in Los Angeles and is active with several new ministries focused on rebuilding lives, churches, and communities.
Q. Why did you begin to address questions about end-of-life planning?
A. My life abruptly changed in 2001. I was waiting for my husband Leander to take me to lunch, and this prompt, former military man didn’t show up. He had had a brain bleed at home. He never regained consciousness and died a week later. I spent that week in the hospital on uncomfortable chairs never wanting to leave his side. It’s what we do, but it was excruciating.
But I did not know what he would have wanted. I probably kept him on life support longer than he would have wanted, waiting for people to make decisions for him, because we had never had the conversation. The only conversations we had had were about living the rest of our lives happy and in love. We’d only been married for three years, but he was truly the love of my life. We shared everything. We had this great love story that was abruptly ended by his sudden death.
And the hardest part was not knowing what he would have wanted. What would his choice have been? Would he have wanted life support? Would he have wanted us singing, bringing people around, parading around his lifeless body? I just did what I thought he would have wanted.
Q. How did you begin teaching others, especially people of faith, about end-of-life issues?
A. After writing my book, I met oncologist Dr. Raleigh Bowden, who founded the Seattle African-American Comfort Program. I joined her as we began focus groups, forums, and just talking about peoples’ ideas on being prepared at end of life. We began interviewing people to ask them about their end-of-life experiences with loved ones and patients. At the time, I was a pastor and I was talking a lot to the church community about these ideas.
Then I got a position with Providence Hospice of Seattle, and part of my function was to help them reach underserved communities, beginning with the African-American community and focusing on the church. I was with them for 3 ½ years. I did a lot of work in the community.
Q. And then you started working in hospice?
A. Yes, I left the church I was pastoring in 2005. I came out of the pulpit and went into hospice work as a diversity director and outreach coordinator. And when I went into the churches, because I was already known in the community, I was given the opportunity to make a statement about end of life from the pulpit.
It was a major platform, because people believed their minister. If their minster or pastor or rabbi or religious leader introduces someone, and then steps aside, and that person stands in the same place they did, the message becomes more acceptable. For many years, that was the work that I did, bringing that information to the church, to the community.
What I found out was it’s not just underserved communities that have difficulty having these conversations. Every community has difficulties having these conversations. I have had adult men, both black and white, cry on my shoulder as I’m talking to them about my book, my personal experience, about the loss of a loved one or someone who is about to pass away. I’ve even had discussions surrounding the difficulty of preparing for someone who has dementia, and now it’s too late for them to make their own decisions. Due to diminished capacity, there is no way that person can sign any document or make choices for themselves that have not already been discussed. It is a very sensitive topic, and ways to have those discussions are still being uncovered. The way that we are talking about it is still evolving.
Q. How did learning about hospice and end-of-life planning help you?
A. I remarried and moved back to California. The man I married was ill and didn’t live long after our marriage. Both my last husband and my father have passed away since I’ve been back in California. And both of them had the benefit of hospice care. Both of them had conversations about what they wanted because I was able to have those conversations with them. The process of releasing them to go to heaven was a lot easier just based on those conversations. I don’t have questions like, what did they want?
Q. Do you have advice for faith leaders who would like to start advance care planning programs?
A. Yes, start them. Everyone has a sensitive spot in their heart for the loss of a loved one. Because everyone will die, having an easy and comfortable way and place for people to discuss their wishes can make these sensitive times easier. That’s the platform that you want to use as the basis for saying it’s okay to talk about this.


America’s Overdose Crisis
Sign up for our five-email course explaining the overdose crisis in America, the state of treatment access, and ways to improve care
Sign up

How Faith Communities Facilitate Conversations Around End-of-Life Concerns
Interviews show the benefits of training and engagement on advance care planning


Why Faith Leaders Are Talking About Dying: A Q&A With Pam Pilote
How she’s helping church congregants advocate for themselves.
Learn More

Why Faith Leaders Are Talking About Dying: A Q&A with Wendy Fenn
How her experience as a hospice chaplain helps educate others.
Learn More

Why Faith Leaders Are Talking About Dying: A Q&A With Y. Khalid Siddiq
How he's overseeing outreach programs and education.
Learn More