Key Findings From 50-State Assessment of Evidence-Based Policymaking
Five states lead in this approach as most others show modest levels of engagement
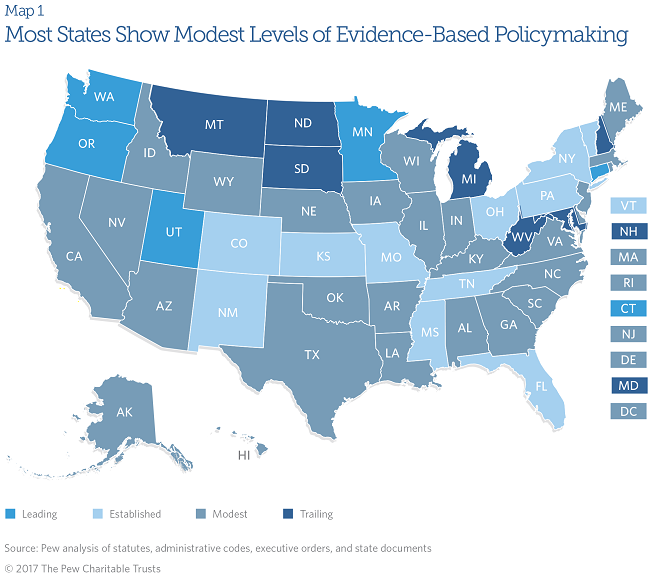
Evidence-based policymaking—the systematic use of findings from program evaluations and outcome analyses to guide government policy and funding decisions—is growing in popularity in state capitols, but information is limited about the extent to which states employ this approach. In a new report, the Pew-MacArthur Results First Initiative identifies five states—Washington, Utah, Minnesota, Connecticut, and Oregon—as leaders in this field. These states demonstrated the most frequent, advanced development of processes and tools for using evidence in policy and budget decisions.
Eleven states show established levels of evidence-based policymaking by pursuing more actions than most others but not as frequently or in as advanced a manner as the leading states. Twenty-seven states and the District of Columbia demonstrate modest engagement, pursuing actions less frequently and in less advanced ways. Seven states are trailing, taking very few evidence-based policymaking actions.
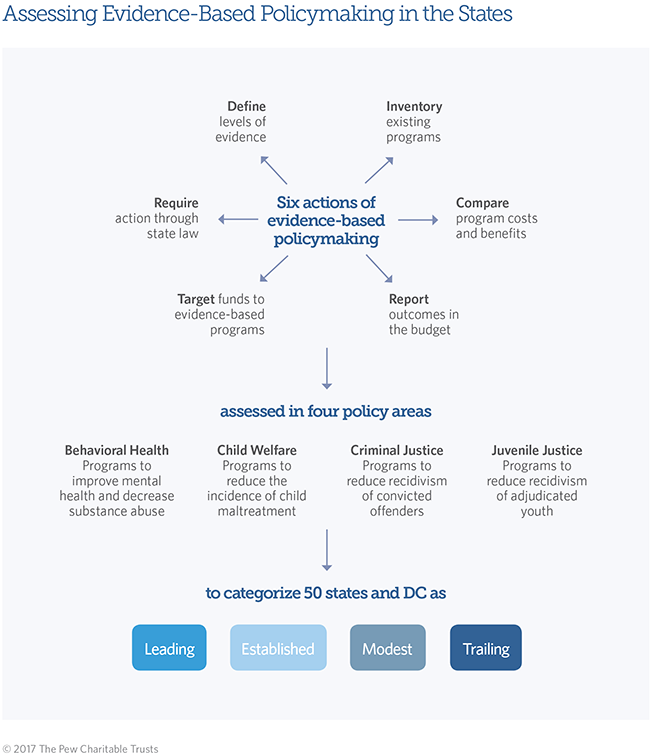
Results First researchers categorized each state and the District of Columbia based on the prevalence and sophistication of six distinct actions of evidence-based policymaking in four policy areas: behavioral health, child welfare, criminal justice, and juvenile justice.
As shown in the figure below, most states have taken some evidence-based policymaking action in at least one human service policy area, but advanced application is less common.
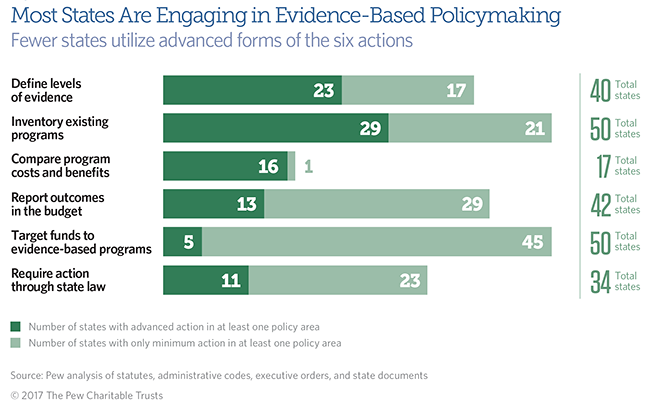
- Thirty-nine states and the District of Columbia have defined at least one level of evidence; 23 of the 40 have created an advanced definition that distinguishes multiple levels of rigor.
- Forty-nine states and the District of Columbia have produced an inventory of state-funded programs; 29 of the 50 have created an advanced inventory that classifies programs by evidence of effectiveness.
- Seventeen states have conducted cost-benefit analyses comparing multiple program options; 16 of the 17 have created an advanced analysis that monetizes benefits to calculate return on investment.
- Forty-one states and the District of Columbia reported or required key outcome data during the fiscal year 2013-17 budget cycles; 13 of the 42 have created advanced budget materials that include findings from program evaluations.
- Forty-nine states and the District of Columbia have a funding mechanism to target funds to evidence-based programs; five of the 50 have created advanced mechanisms to dedicate at least 50 percent of program funds for a specific policy area to these initiatives.
- Thirty-three states and the District of Columbia have a minimum framework of laws to support one or more of the five advanced actions listed above; 11 states have created an advanced framework with laws to support two or more advanced actions.
Despite the myriad successes found in states, challenges in evidence-based policymaking engagement persist. The report identifies how policymakers and staff can address these challenges by educating stakeholders on the value of this approach, developing a strong data infrastructure, and enhancing capacity to fund and implement programs shown to be effective.
As governments continue to face fiscal pressures to produce more value for each dollar they spend, states would be well served to engage in all six actions of evidence-based policymaking to build a better future.
Sara Dube is the director and Darcy White is an officer with the Pew-MacArthur Results First Initiative.


America’s Overdose Crisis
Sign up for our five-email course explaining the overdose crisis in America, the state of treatment access, and ways to improve care
Sign up

States Engage in Evidence-Based Policymaking
A national assessment


This video is hosted by YouTube. In order to view it, you must consent to the use of “Marketing Cookies” by updating your preferences in the Cookie Settings link below. View on YouTube
This video is hosted by YouTube. In order to view it, you must consent to the use of “Marketing Cookies” by updating your preferences in the Cookie Settings link below. View on YouTube